This piece will cover Blockchain Alternatives to Proof of Work. Proof of Work consumes a large amount of computing power and requires costly mining equipment.
Thankfully, Proof of Stake and its variants, as well as other hybrid models, provide a faster and more secure method of consensus. These alternatives will determine how blockchain technology will be adopted sustainably across the globe in the future.
What is Proof of Work (PoW)?
Proof of Work (PoW) remains the first and most widely used consensus mechanism in blockchain networks, beginning with Bitcoin. The essence of PoW is to facilitate agreement on the state of the blockchain across all participants in a decentralized network without the use of a central authority.
This is done by having participants, called miners, authenticate and add new blocks to the blockchain by solving complicated mathematical puzzles. The puzzles are difficult to solve, but they are easy to verify, which provides a secure and trustless environment.
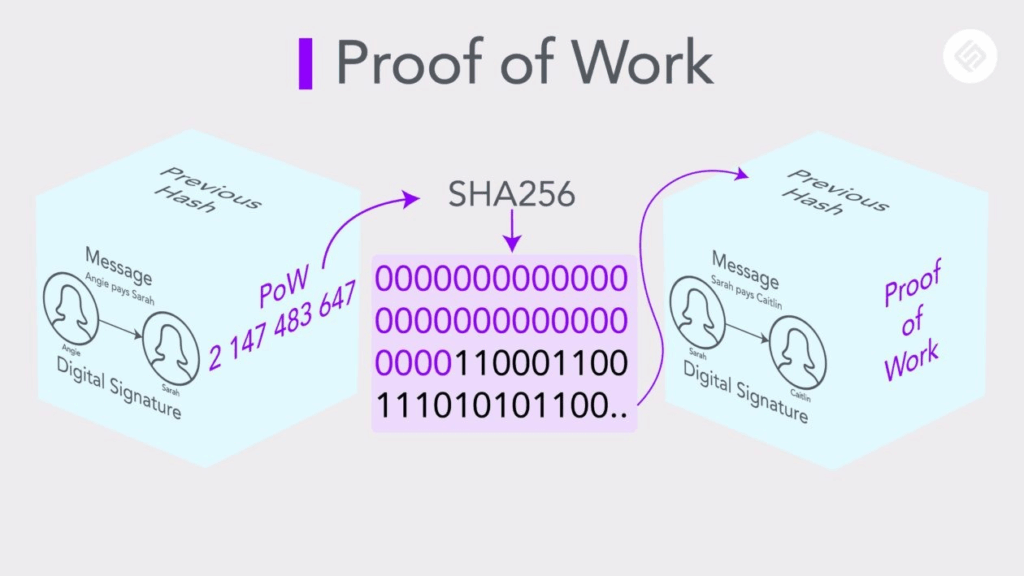
PoW’s most significant advantage rests on its security: to attempt to successfully manipulate the blockchain is to alter a block and subsequently all blocks which makes it nearly impossible and infeasible to do so.
This also makes PoW resistant to fraud and double-spending. In addition to this, PoW assists with the decentralization of the network since any person with enough computational power can join and assist with block validation.
Yet, Proof of Work has major disadvantages, especially the issues of scalability and energy consumption. The process of mining involves enormous quantities of electricity because of the level of competition among miners.
The expensive operational costs and the resulting environmental impact are also considerable. Furthermore, this process also limits the number of transactions the network is able to process, resulting in considerable delays in processing transactions, especially in comparison to newer consensus methods. Regardless of the challenges,
Proof of Work is still relevant and critical to the blockchain technology groundwork and serves the purpose of comparison to the newer alternatives that are more energy-efficient, such as Proof of Stake and Proof of Authority.
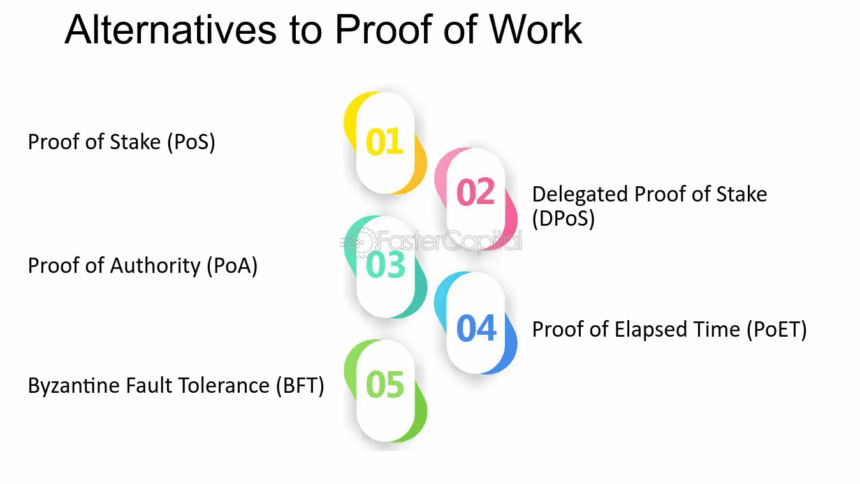
Blockchain Alternatives to Proof of Work
Proof of Stake (PoS)
- Validators are selected based on the amount of crypto they own and “stake.”
- More energy efficient than PoW.
- Minimizes centralization and excess costs of mining hardware.
Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS)
- Token holders elect a small number of delegates to validate transactions.
- More rapid and scalable than PoW and standard PoS.
- Implemented on blockchains like EOS and Tron.
Proof of Authority (PoA)
- Validators are trusted and set to create new blocks.
- Quite efficient and rapid.
- Optimal for private or consortium blockchains.
Proof of Burn (PoB)
- Miners “burn” tokens (send to an unspendable address) to earn the right to mine.
- Low energy expenditure and lower PoB Burn network longevity.
Proof of Space / Proof of Capacity (PoC)
- Mining power is based on available disk space rather than computational capacity.
- Less energy destructive than PoW.
- Implemented by projects like Chia.
Hybrid Consensus (PoW + PoS)
- Aimed at balancing security and decentralization within a range of efficiency levels.
- Decred (DCR) is a case in point.
Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT)
- Instead of mining, validators utilize a voting paradigm to consonance.
- Transactions achieve high throughput with reduced latency.
- Suitable for private or permissioned blockchains.
Tips For Safe Blockchain Alternatives to Proof of Work
Choose Established Networks
- Use blockchains that are trusted and have good community backing.
- Examples: Ethereum 2.0 (PoS), Cardano (PoS), EOS (DPoS).
Validator/Delegate Reputation
- In PoS or DPoS systems, check the validators’ histories. Good validators are those with little downtime.
- Stick to validators to mitigate the risk of fraud.
Consensus Mechanism Security
- Know how blockchains tackle the risks of double-spending and 51% attacks.
- PoS, DPoS, and PoA reduce energy usage but require thorough validator selection.
Hold a Variety of Assets
- Keep your assets on a few different blockchains instead of a single chain.
- This helps mitigate the risk of a failing network.
Protocol Upgrades
- Security and scalability improvements are the reason many PoS or hybrid networks deploy updates.
- Keep an eye on official sources, and remember to update your wallets or staking nodes.
Wallet Security
- When staking or holding tokens, always use a hardware or reputable software wallet.
- Keep private keys safe and remove any potential access to them.
Future of Blockchain Consensus
The development of blockchain consensus is prioritizing energy efficiency, scalability, security, and cost-effectiveness in overcoming the drawbacks of conventional Proof of Work (PoW). Faster processing capabilities, lower energy requirements, and reduced hardware dependency are enticing characteristics of Proof of Stake (PoS), Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), as well as hybrid systems.
Aside from technological advancements in sharding and layer-2 and inter-chain interoperability, there is growing networking and blockchain efficiency as system innovations. On top of that, consensus mechanisms are starting to embrace blockchain’s expanded usability in more diverse- and regulated- environments and in varied industries including finance, supply chains, and healthcare and governance systems.
Demonstrated need, higher expectations, and a growing need for cost reduction will dominate the evolution of consensus mechanisms and other systems underpinning next generation blockchain.
Pros & Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Energy-efficient, lower hardware costs, reduces centralization risk | Wealth concentration risk, validator penalties (slashing) |
| High scalability, fast transactions, democratic voting | Centralization risk if few delegates dominate, less decentralized |
| Very fast and efficient, suitable for private networks | Requires trusted validators, less decentralized |
| Reduces energy usage, aligns incentives with network longevity | Slow adoption, complex for beginners |
| Environmentally friendly, low energy consumption | Requires large storage, potential hardware bottlenecks |
| Combines security of PoW with efficiency of PoS | Complex implementation, can be harder to understand |
| High throughput, low latency, secure for private networks | Not fully decentralized, limited scalability for very large networks |
Conclusion
In summary, blockchain alternatives to Proof of Work provide more sustainable, efficient, and scalable solutions to modern decentralized networks.
Proof of Stake, Delegated PoS, Proof of Authority, and hybrid consensus mechanisms lowered energy cost, increased transaction speeds, and stayed secure while reducing the dependence on high-priced computing resources.
With the development of blockchain technology, the need for these alternatives to more eco-balanced, elevated-performance, and readily usable networks is definitely growing.
With respect to the particular goals of a blockchain—decentralization, scale, security, or sustainability—the appropriate consensus mechanism can be selected, which brings versatility and greater accessibility to the blockchain.
FAQ
Can private blockchains use alternatives like PoA or PBFT?
Absolutely. PoA and PBFT are ideal for private or consortium blockchains due to their high speed and low energy requirements.
Which alternative is the most eco-friendly?
Proof of Stake and Proof of Space/Capacity are currently the most environmentally friendly alternatives to PoW.
Are hybrid consensus models effective?
Yes, hybrid models combine PW and PoS benefits, balancing security, efficiency, and decentralization.