This article will examine the various alternatives to the Proof of Work consensus method. While Proof of Work supports Bitcoin and other major cryptocurrencies
Its high energy consumption coupled with difficulty in scalability has incentivized the creation of more efficient consensus methods.
We will look at alternatives which do not compromise on security, decentralization, and speed while avoiding the inconveniences of traditional mining.
Overview
Blockchain is the new technology that allows decentralized systems to be truly decentralized. Cryptocurrencies and supply chain management use blockchains for their transparency, immutability, and security.
Every blockchain is based on a consensus mechanism that allows all the distributed participants of the network to agree on the state of the blockchain ledger.
Proof of Work (PoW) is the oldest and most known consensus mechanism, but it is expensive and energy inefficient.
Fortunately, there are a number more PoW energy efficient options available in the blockchain ecosystem that are able to achieve security and decentralization in a more streamlined manner.
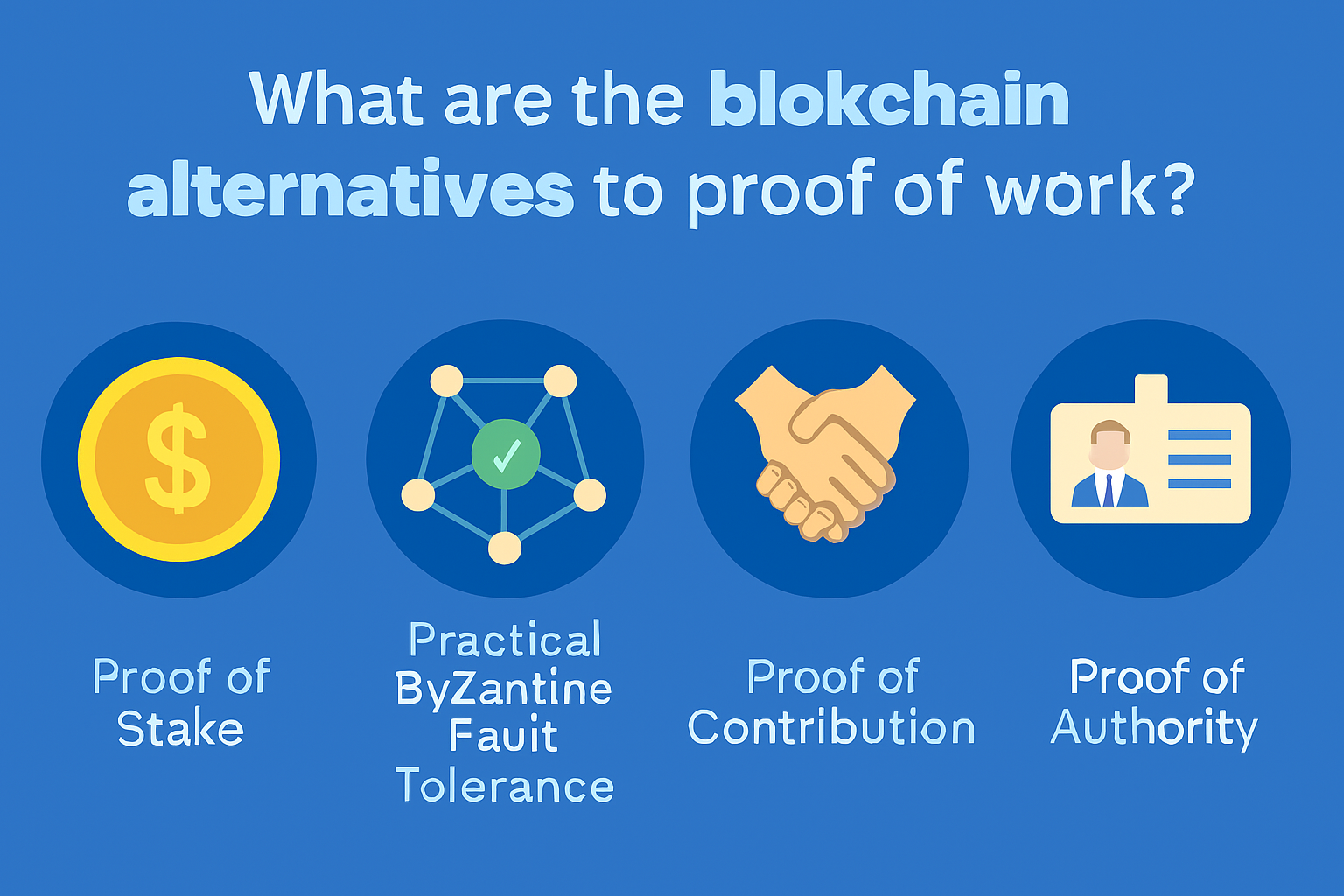
What are the blockchain alternatives to proof of work
PoW is processor, and energy expensive primarily because it consumes an enormous amount of energy. An example of this is Bitcoin, whose network consumes as much energy as countries.
It is true that PoW has a strong and secure blockchain, but that is expensive. It is expensive because it relies on miners to solve complex and high energy consuming mathematical puzzles that then validate and confirm each transaction.
Furthermore, the system is heavily biased and favors participants (or ‘players’) that own specialized and expensive PoW mining hardware (aka ‘ASIC miners’).
This leads to exploitative centralization and monopolization of PoW mining, as it is mining, and power, that is redistributed, as well as energy, to participants as network rewards.
This leads to the centralization ‘trap’ of wealth and energy consumption, which is being further loopholed by crypto regulation.
It is the hopes of the blockchain community that this can be solved by the implementation of new consensus systems that are blockchain environmentally friendly and scalable.
Proof of Stake (PoS)
PoS is the most notable alternative to Proof of Work (PoW). PoS determines which validators get to create the next block based on which validators have the most coins and which ones are willing to “stake” their coins as collateral.
- Energy Efficiency: Since PoS does not require validators to solve complex puzzles, it consumes a lot less energy.
- Security: Honest behavior is reinforced by the validator losing their staked coins when acting maliciously.
- Examples: Ethereum transitioned to PoS in 2022 during the “Merge” and was able to significantly decrease its energy footprint. Other platforms PoS variants are Cardano and Solana.
Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS)
DPoS expands on PoS by adding a voting mechanism. Coin holders vote to select a small number of delegates who then validate the transactions and secure the network.
- Efficiency: DPoS is able to process transactions at a faster rate than traditional PoS as there are less nodes involved in block validation.
- Governance: Through voting, token holders participate in network governance.
- Examples: DPoS is also used by EOS, Tron, and Steem to reduce energy usage while maintaining high throughput.
Proof of Authority (PoA)
As of October 2023, Proof of Authority (PoA) is a consensus mechanism in which validators, not the entire network, authenticate transactions. Validators’ identities are known publicly and are therefore accountable for their actions.
- Low Energy Usage: The system has low computational requirements and therefore low energy requirements.
- Private Networks: PoA is applicable in blockchains as in enterprises and consortiums where trust is a little established.
- Examples: PoA is used in VeChain and some Ethreum-based private networks for scalability and efficiency.
Proof of Space (PoSpace) and Proof of Capacity
Proof of Space, otherwise Proof of Capacity, uses unused storage space rather than computational power. Participants in the network allocate some disk space for cryptographic data, and the network randomly picks a winner to create the next block.
- Sustainable: PoSpace is a low energy, sustainable option because it uses storage space instead of electricity for computation.
- Security: The large storage allocation needed for validation provides data for honest participation.
- Examples: Chia network uses PoSpace as a positive alternative to traditional PoW systems.
Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT)
A consensus theorem PBFT has been developed to fault tolerate within distributed systems and it is to bring consensus among a network of untrusting (malicious) nodes.
- High Throughput: Over one hundred to one thousand transactions can be handled within a second using PBFT.
- Trust Model: Validated trust that members within a permissioned network view and interact.
- Examples: For both enterprise and scalable solutions, PBFT, and its variants are used by Hyperledger Fabric and Zilliqa.
Hybrid Consensus Models
To optimize for performance, security, and energy efficiency, some blockchains use a combination of different mechanisms. For example, some might use PoS to create blocks and PoA to validate transactions, thereby achieving some level of decentralization and speed.
- Flexibility: Hybrid models reduce single points of failure and can adjust to varying network needs.
- Examples: Decred combines PoW and PoS to provide security while allowing both miners and stakeholders to actively participate.
Comparative Analysis
| Consensus Mechanism | Energy Use | Decentralization | Scalability | Notable Projects |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PoW | Very High | High | Low | Bitcoin |
| PoS | Low | High | Moderate | Ethereum, Cardano |
| DPoS | Low | Moderate | High | EOS, TRON |
| PoA | Very Low | Low | Very High | VeChain |
| PoC | Low | Moderate | Moderate | Chia |
| PoB | Low | Moderate | Low | Slimcoin |
| PoET | Very Low | Low-Moderate | High | Hyperledger |
| BFT | Low | Moderate | High | Cosmos |
Conclusion
Alternatives to PoW are being explored due to its challenges in scalability and environmental factors.
For different use cases, PoS, Delegate PoS, Proof of Authority, and PBFT provide energy efficient mechanisms from private enterprise networks to public cryptocurrencies.
As blockchain technology progresses, these alternatives will help create a scalable and sustainable future.
FAQ
What are the blockchain alternatives to proof of work
Proof of Stake selects validators to create new blocks based on the number of coins they “stake” as collateral.
What is Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS)?
Delegated Proof of Stake allows coin holders to vote for a small group of delegates who validate transactions.
What is Proof of Space (PoSpace) or Proof of Capacity?
Proof of Space uses unused storage space to validate transactions instead of computational power. It is sustainable, requires less energy, and is used by blockchains like Chia Network.
Are there hybrid blockchain consensus models?
Yes, hybrid models combine multiple mechanisms for better performance, security, and decentralization.
Which alternative is the most energy-efficient?
Proof of Stake (PoS) and Proof of Authority (PoA) are among the most energy-efficient alternatives to PoW because they do not rely on energy-intensive mining operations.