In this article, I’ll discuss the Blockchain For Business is reshaping core business processes across sectors.
By bringing tamper-proof records, shared visibility, and programmable logic to the table, blockchain is streamlining supply chains, safeguarding patient records in healthcare, and automating contractual agreements.
I’ll outline the underlying characteristics that empower these transformations, highlight relevant case studies, and explain why the race toward decentralized solutions is accelerating as companies seek an edge in the digital-first marketplace.
Key Point & Blockchain For Business List
| Use Case | Key Point |
|---|---|
| Supply Chain Management | Ensures transparent, real-time tracking of goods from origin to destination. |
| Healthcare Data Management | Provides secure and interoperable access to patient records across systems. |
| Smart Contracts | Enables automated, trustless execution of agreements without intermediaries. |
| Digital Identity Verification | Offers tamper-proof, user-controlled identity verification across platforms. |
| Voting Systems | Guarantees secure, transparent, and tamper-resistant digital voting. |
| Energy Trading Platforms | Facilitates peer-to-peer energy trade with transparent pricing and settlement. |
| Digital Rights Management | Secures intellectual property rights and automates royalty distribution. |
| Food Safety & Traceability | Tracks food production and delivery to ensure safety and prevent fraud. |
| Charity & Donation Tracking | Increases trust by transparently tracking fund flow to intended beneficiaries. |
1.Supply Chain Management
Supply chain management stands out as a flagship application of blockchain technology because it replaces outdated traceability models with a system that delivers real-time visibility, tamper-proof records, and seamless, trust-free collaboration among all stakeholders.

Each shipment, transaction, and custody change is logged in an immutable chain, thereby curtailing fraud, cutting operating costs, and minimizing contractual disputes. The distributed ledger allows participants to authenticate products and verify regulatory compliance independently, eliminating dependence on a central verifier.
This heightened transparency and traceability is particularly critical for sectors that navigate intricate, multi-country logistics, positioning blockchain as a compelling, durable backbone for next-generation supply chains.
Supply Chain Management Features
- Transparency & Traceability: Every step of a product’s journey is recorded immutably, enabling verification of its source and deterring counterfeits.
- Real-Time Auditing: All authorized stakeholders see a shared ledger that updates instantly, minimizing discrepancies and the need for lengthy reconciliations.
- Smart Contracts: Automated code executes actions like payments or inventory adjustments as soon as delivery criteria are confirmed.
2.Healthcare Data Management
Blockchain technology transforms healthcare data management by safeguarding patient information and granting secure, selective access to different providers. With its distributed ledger system, blockchain preserves data accuracy, protects privacy, and delivers information instantaneously, thus removing vulnerabilities to alteration and unauthorized entry.

This security profile makes the framework highly suitable for storing electronic health records, supporting clinical trial data, and streamlining insurance reimbursement workflows. The system’s crowning advantage is patient empowerment: individuals can control their health records, granting data-sharing consent that enhances care continuity and cuts the administrative burdens faced by organizations.
Healthcare Data Management Features
- Secure Data Sharing: Patients govern access to their health records through encrypted, permissioned ledgers that grant precise control.
- Interoperability: Blockchain links disparate healthcare systems, allowing seamless data flow that enhances diagnosis and treatment continuity.
- Tamper-Proof Records: Data entered onto the chain is immutable, safeguarding patient information and research findings for compliance and patient safety.
3.Smart Contracts
Smart contracts form the backbone of blockchain-enabled business solutions. By codifying agreements into self-executing lines of code, they guarantee accuracy, visibility, and independence from third-party validators.
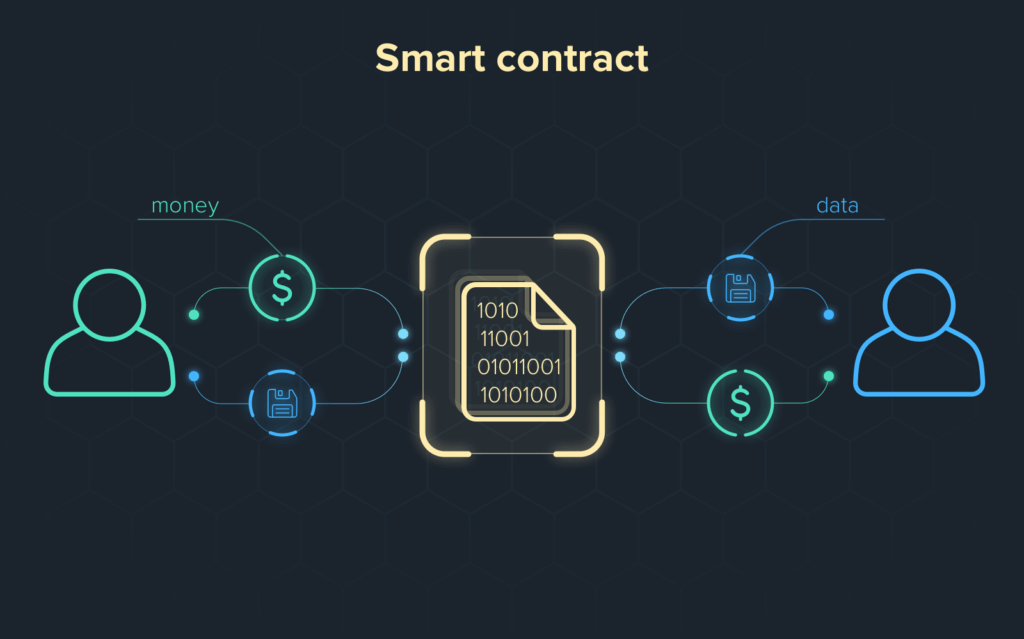
As a result, organizations experience shorter transaction cycles, reduced overhead, and a marked decline in human error. The core business benefit is programmable trust—actions will only trigger when all agreed-upon parameters are satisfied. This intrinsic feature minimizes compliance risks and curbs potential disputes.
Consequently, smart contracts are well-suited for automating supply chain logistics, financial transactions, and legal workflows, allowing firms to accelerate operations and expand confidently across a worldwide network of partners.
Smart Contracts Features
- Automation: Contracts self-execute once designated conditions are satisfied, removing the need for middlemen to enforce terms.
- Cost-Efficiency: Administrative burdens and delays in contract performance are cut, leading to faster, cheaper transactions.
- Trustless Systems: Transactions can occur securely between parties with no prior relationship, since enforcement is guaranteed by code rather than trust.
4.Digital Identity Verification
Digital identity verification is becoming an essential blockchain service for companies, offering safe, self-sovereign identity proof across online environments. In contrast to traditional models, blockchain empowers users to hold and present certified identity data while keeping private information hidden.

For firms, this translates to quicker account setup, lower fraud risk, and alignment with privacy and data protection laws. The core advantage lies in verification that is trustless—meaning individuals can authenticate each other without a governing body—making the approach particularly fitting for finance, online retail, and any sector that demands secure, scalable proof of identity.
Digital Identity Verification Features
- Self-Sovereign Identity: Individuals retain ownership of their identity data, using decentralized identifiers to control what is shared and with whom.
- KYC Simplification: Organizations reduce onboarding friction by accepting reusable, previously verified identity credentials that meet Know Your Customer (KYC) obligations.
- Fraud Prevention: Permanent identity logs cut down on impersonation and identity theft by making tampering almost impossible.
5.Voting Systems
Voting systems built on blockchain represent a major advance for businesses, particularly in governance, shareholder resolutions, and overall transparency.

The technology guarantees that each ballot is unalterable, verifiable, and openly traceable while preserving voter confidentiality. This feature alone prevents any tampering and fosters confidence in online polls.
The real strategic advantage for companies is the capacity for secure, remote involvement in decision-making, which cuts administration costs and elevates stakeholder participation. The approach converts conventional voting into a realtime, fully auditable procedure that suits corporations, cooperatives, and any organization that operates on decentralized principles.
Voting Systems Features
- Tamper-Resistant Logs: Once results are recorded, they cannot be altered or erased, protecting electoral integrity.
- Voter Verification: Each ballot is tied to a validated, unique citizen identity, blocking any chance of double voting.
- Transparency: Open ledgers can be independently audited, boosting public confidence in the voting process.
6.Energy Trading Platforms
New blockchain-based energy trading platforms empower companies to trade power directly with one another, skipping legacy utilities and cutting transaction costs. The distributed ledger guarantees transparent pricing, instantaneous settlement, and secure, immutable records of every kilowatt-hour.

A standout benefit for firms is the chance to join peer-to-peer markets and sell surplus renewable output—whether from rooftop solar or wind turbines—turning spare capacity into revenue. The result is a more flexible and responsive energy grid: one where profit motives, ecological responsibility, and efficiency all converge, enabling enterprises to fine-tune consumption and lower bills simultaneously.
Energy Trading Platforms Features
- Peer-to-Peer Energy Exchange: Community members can buy and sell surplus green power without having to go through utilities.
- Real-Time Settlements: Automatically executed smart contracts handle billing and delivery confirmations in seconds.
- Grid Efficiency: Local trades support microgrids, cutting transmission losses and balancing supply and demand.
7.Digital Rights Management
Blockchain-based DRM gives firms a resilient framework to monitor, license, and authenticate ownership of digital assets. By embedding smart contracts, creators and rights owners receive immediate, automatic payment every time their material is viewed or distributed.

The core advantage is the removal of centralized gatekeepers; rights holders gain full autonomy to defend their works. Consequently, industries like media, publishing, and entertainment can develop clear, frictionless monetization streams, curbing unauthorized redistribution and ensuring equitable returns on creative investment.
Digital Rights Management Features
- Ownership Verification: Creators can record original works on-chain, establishing clear proof of authorship and title.
- Royalty Automation: Payments to artists and rights owners are triggered by usage, flowing automatically through smart contracts.
- Piracy Control: Permanent logs track unauthorized distribution, making it easier to enforce copyright.
8.Food Safety & Traceability
Ensuring food safety and traceability is an ideal use of blockchain technology, delivering complete visibility throughout the entire supply chain. By documenting each movement—from the farm gate to the consumer plate—on an unchangeable ledger, blockchain allows quick pinpointing of contamination origins and expedites targeted recalls.

For companies, the standout advantage is the ability to cultivate consumer confidence via auditor-ready, tamper-proof transparency while streamlining adherence to regulatory mandates. This capability lowers spoilage, curbs counterfeiting, and bolsters brand integrity, positioning blockchain as a vital component of today’s food quality assurance toolkit.
Food Safety & Traceability Features
- Source Authentication: Blockchain follows every food item from the farm to the consumer, verifying its origin and quality.
- Recall Efficiency: Contaminated batches can be traced and isolated in minutes, minimizing health risks and financial losses.
- Regulatory Compliance: Transparent, tamper-proof logs satisfy food safety regulators and simplify audits.
9.Charity & Donation Tracking
Using blockchain to track charity and donations delivers unparalleled clarity and responsibility to philanthropy linked to business goals. Each financial flow is securely logged, empowering donors to follow money straight to its destination without gatekeepers. Companies gain a powerful edge through credible impact accounts—proving corporate social responsibility with indisputable evidence.

This fosters public trust, strengthens brand reputation, and guarantees prudent fund stewardship. By cutting the risk of misallocation, boosting donor assurance, and allowing instant auditing, blockchain redesigns how entities record, manage, and report their charitable giving.
Charity & Donation Tracking Features
- Donation Transparency: Supporters can follow the journey of their gifts, creating trust through visible, traceable spending.
- Reduced Misuse: Distributed records lock in transactions, making it difficult for anyone to reroute funds for improper use.
- Real-Time Impact Reporting: Contributors receive immediate notifications showing exactly where their money has gone and how it’s making a difference.
Conclusion
In summary, blockchain is fundamentally altering operational foundations for companies, delivering security, visibility, and efficiency at scale. Smart contracts, identity verification, asset tracking, and verifiable trust are no longer experimental; they’re embedded, driving enhanced accountability and creative problem-solving.
The distributed architecture diminishes dependence on middlemen, trims expenses, and fortifies data accuracy. As organizations pursue comprehensive digital transformation and seek a competitive edge on the world stage, the choice to adopt blockchain becomes a decisive pivot—one that positions them for more agile, transparent, and durable business models.
FAQ
What is blockchain for business?
Blockchain for business refers to the use of distributed ledger technology to improve transparency, security, and efficiency in business operations such as supply chains, finance, healthcare, and identity verification.
How is blockchain different from traditional databases?
Unlike traditional databases, blockchain is decentralized, immutable, and shared among multiple parties. Once data is recorded, it cannot be altered, providing trust without a central authority.
Is blockchain secure for storing sensitive business data?
Yes, blockchain uses advanced cryptographic techniques and consensus mechanisms to secure data. Permissioned blockchains further enhance security by restricting access to verified participants only.