Fully Homomorphic Encryption (FHE), a cryptographic innovation that enables data processing while maintaining encryption, will be covered in this article.
FHE is regarded as the “Holy Grail” of privacy since it allows DeFi platforms to conduct computations without disclosing private user data. Through improved security, privacy, and trustless interactions, this technology has the potential to revolutionize decentralized banking.
What is Fully Homomorphic Encryption (FHE)?
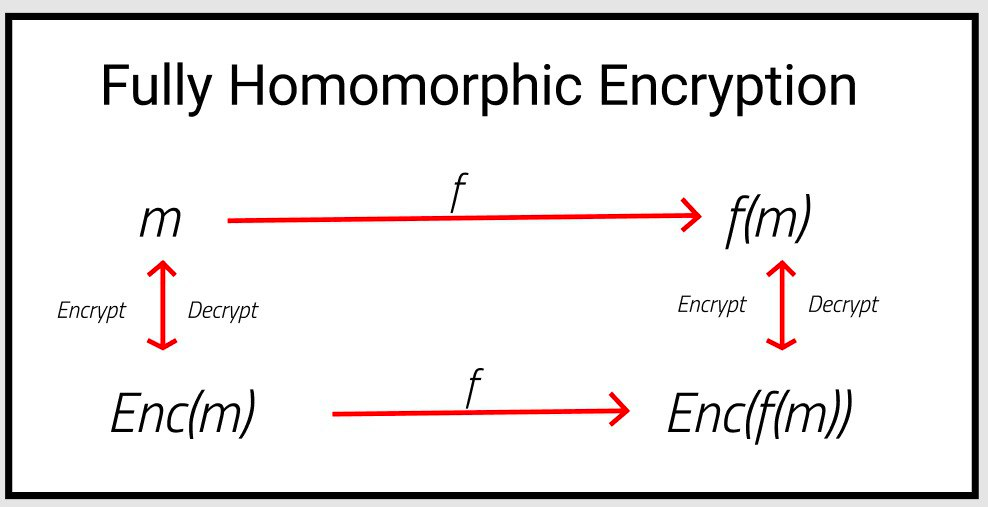
A sophisticated cryptographic method called Fully Homomorphic Encryption (FHE) enables calculations to be done directly on encrypted material without ever having to decrypt it. FHE guarantees that sensitive data stays private during computing, as contrast to standard encryption, which requires data to be decrypted before processing—exposing it to possible hazards.

This implies that ciphertext can be used to perform operations such as addition, multiplication, and more intricate functions, resulting in an encrypted result that, when decrypted, is identical to the result as if it were calculated using the original data. With its revolutionary potential for secure cloud computing, private DeFi transactions, and privacy-preserving data analytics, FHE is regarded as the “Holy Grail” of privacy.
How FHE Works (Simplified Explanation)
Data Encryption:
- Before a user sends sensitive information to a server or a blockchain, they must first encrypt it.
- The server cannot see or understand the actual data.
Encrypted Computation:
- The server can process the encrypted data (ciphertext) as is.
- Addition and multiplication, as well as more complex functions, can be done without the data being decrypted.
Encrypted Results:
- The outcome of the computations is still encrypted and remains confidential.
Decryption by Owner:
- Only the individual with the private key can unlock the result.
- The result is the same as what would have been computed on the actual data.
Zero Data Exposure:
- Never is the raw data exposed, this makes it completely secure and private.
Why is FHE important for DeFi?
Privacy-Preserving Transactions:
- Defi protocols can be used without revealing financial balances, trading history, or other personal details.
Confidential Smart Contracts:
- Strategies, inputs, and outcomes can be kept private while smart contracts run complex logic on encrypted data.
Enhanced Security:
- With data kept encrypted using FHE at all times, the chances of hacks, leaks, and unauthorized access is significantly lower.
Regulatory Compliance:
- FHE helps platforms remain compliant legally and in the reporting process while keeping and processing data in a privacy-preserving manner.
Trustless Environment:
- Stronger decentralization and user sovereignty, as data does not need to be trusted with intermediaries.
Enables Innovative DeFi Products:
- Private lending, encrypted analytics, and multi-party computations allow for further advanced financial services.
Advantages of FHE for DeFi
Total Privacy:
- Helps DeFi platforms process user data while never seeing the data, keeping the user’s financial activities private.
Increased Security:
- With FHE, sensitive information is protected from hacking, leakage, and unauthorized access, thereby minimizing the risk involved with DeFi.
Regulatory Friendly:
- FHE allows for the completion of privacy transactions while still being able to satisfy regulatory mandates to ensure the right to both privacy and safety.
Smart Contracts Are Confidential:
- Smart contracts are able to execute embedded logic through encrypted inputs, which keeps strategies, amounts, and trading activities private.
New DeFi Innovations:
- FHE allows for new services like private lending and encrypted data analytics. Also, it gives multi-party computation to DeFi.
No Trust Needed:
- Data is not given to intermediaries, making the system decentralized and allowing for no trust to be needed.
Challenges and Limitations

High Computational Overhead.
- The FHE requires so much computing power that they can potentially slow down transaction completions.
Scalability Issues.
- The impact FHE has on current performance might make large DeFi platforms large-scale implementations of FHE inefficient.
Complex Implementation.
- Custom solutions are required to add FHE functionality to smart contracts and blockchain protocols.
Latency.
- The experience in real-time DeFi applications can be negatively affected when encrypted computations are processed.
Limited Practical Adoption.
- FHE is still in the majority of pilot projects.
Cost.
- Infrastructure and compute costs are high in FHEs making their use unfeasible to small DeFi projects.
Risk & Consider
erformance Trade-offs
- DeFi platforms may experience an overall decrease in efficiency due to the increased time FHE take to process transactions. FHE may create a increase in processing time it could take to complete the transaction.
Technical Complexity
- Errors and vulnerabilities in the implementation of FHE could occurr due to the extensive knowledge in the area of cryptography that is needed by developers.
Integration Challenges
- There could be a significant delay in the deployment due to the fact that existing DeFi protocols encrypted models and that may mean the protocols will need to be designed from scratch.
Cost Implications
- For DeFi services to be utilized by users FHE based services will need to be maintained and with a high operational cost that will be due to an increase in computational cost which will be incurred.
Limited Ecosystem Support
- Since FHE tools and libraries are still developing maintenance and updates may be difficult.
Regulatory Uncertainty
- There could be a lot of questions surrounding compliance in the jurisdictions for the governments that may have stricter laws and may be cash based.
Real-World Applications and Projects
Encrypted Lending Platforms
- With FHE technology, smart contracts can execute payment and calculate interest, collateral, and risk without revealing sensitive information to the borrower and lender, thus creating a transactional blind process.
Privacy-Preserving Trading
- In decentralized exchanges (DEXs), FHE can be applied to execute trading and order matching without exposing user balance, position, and trading strategy to the public.
Confidential DeFi Derivatives
- Platforms that offer derivatives or options can utilize FHE to calculate (trade) encrypted data (compete) in the market, thereby safeguarding the trade secrets and market strategy.
Cross-Platform Data Sharing
- The FHE technology can be applied in DeFi apps to share analytics, credit scoring, or yield optimization data without exposing user data- even encrypted data can be pivotally used.
Enterprise & Institutional DeFi Adoption
- The FHE technology can be applied to integrated the decentralized finance (DeFi) technology into the banking system of big financial institutions & to comply with the data privacy policy and merge the traditional finance with blockchain technology.
Pilot Projects and Collaborations
- Various projects are taking the initiative, especially Zama, Enigma (Secret Network), and Duality Technologies, acted as a trailblazer on the integration of FHE with blockchain and DeFi. It offers a proof-of-concept for the privacy-preserving smart contracts.
Future Outlook
For the future of DeFi, Fully Homomorphic Encryption (FHE) has enormous potential to revolutionize the processing and security of financial data.
More platforms are likely to implement privacy-preserving protocols without sacrificing performance as computing efficiency increases and optimized FHE algorithms appear. Secure multi-party computations, private analytics at scale, and completely confidential smart contracts may all be made possible by this.
In order to support such privacy technology, regulatory frameworks may change, promoting innovation while upholding compliance. With its unmatched secrecy, trustlessness, and security, FHE has the potential to become a regular feature in DeFi over time, completely changing the decentralized finance scene.
Pros & Cons
Pros of FHE in DeFi Pros & Cons
- Total confidentiality — FHE allows computations on encrypted data without revealing the identity of the user or the data of the transactions.
- Ensured Compliance — Maintaining the functionality of DeFi services, FHE provisions legal disclosures (i.e., Data Protection and Privacy Regulations).
- Supplemented Protection — FHE decreases the occurrence of hacks, front-running, and the unwarranted disclosure of strategies trading.
- Facilitates Confidential Financial Offerings — FHE will facilitate the offering of other financial offerings, i.e., confidential loans, derivatives, and analytics across multiple platforms.
- Increased Trust — FHE will help increase trust in DeFi services and offer participants all the privacy ecosystem protections that are provided in the traditional finance system.
Cons of FHE in DeFi Pros & Cons
- Resource Intensive — These services will be a drain on computing services, and will take a significant amount of time to complete.
- Current technological restrictions — Today’s technologies will be challenged when trying to meet the needs of these services.
- Incompatibility with Existing Smart Contracts — FHE technologies will be incompatible with most existing Smart Contracts and Blockchain Protocols.
- Increased Cost — The development of these technologies will require significant changes in the current norm.
- Currently Restricted Scope — FHE technologies are currently new and unproven, with scarce fully functional live projects to draw data or insights from.
Conclusion
A ground-breaking development in privacy and security, Fully Homomorphic Encryption (FHE) enables DeFi devices to process data without ever disclosing it. FHE guarantees total confidentiality, fortifies security, and promotes trustless interactions—all essential components of decentralized finance—by permitting calculations on encrypted data.
Even if there are still issues like complicated implementation and large computing needs, continued research and technical advancements are gradually making FHE more useful. FHE has the potential to revolutionize privacy standards in DeFi as adoption increases, opening up cutting-edge financial services while protecting sensitive data for customers everywhere.
FAQ
What is Fully Homomorphic Encryption (FHE)?
FHE is a cryptographic method that allows computations on encrypted data without decrypting it, ensuring complete privacy and security during processing.
How is FHE different from traditional encryption?
Traditional encryption requires data to be decrypted before computation, exposing it to risk. FHE keeps data encrypted throughout the entire process.
Why is FHE important for DeFi?
It enables confidential transactions, privacy-preserving smart contracts, and secure analytics, allowing DeFi users to maintain privacy without sacrificing functionality.
What challenges does FHE face?
FHE is computationally intensive, complex to implement, and may increase transaction latency and operational costs. Scalability and ecosystem support are also limited.
Can FHE be widely adopted in the near future?
Yes, as algorithms improve and computing power grows, adoption is expected to rise, enabling more secure and privacy-focused DeFi applications.