In this article, I will discuss the Best in Technology for Cybersecurity, emphasizing the leading tools and technologies transforming modern digital defenses.
These technologies are crucial in preemptive cyberattack prevention, securing information, and protecting networks in real-time over cloud, edge, and hybrid ecosystems.
The use of Artificial Intelligence for threat detection within cybersecurity systems, post-quantum encryption, and Zero Trust models are some of the most advanced and effective tools shaping digital defenses.
Key Point & Best in Technology for Cybersecurity
| Cybersecurity Technology | Key Point |
|---|---|
| AI-Driven Threat Detection & Response | Uses machine learning to identify and respond to threats in real time, reducing manual intervention. |
| Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) | Enforces strict identity verification for every user and device, regardless of network location. |
| Extended Detection and Response (XDR) | Unifies multiple security tools into one platform for enhanced visibility and faster incident response. |
| Cloud-Native Application Protection Platforms (CNAPP) | Secures applications throughout their lifecycle across multi-cloud environments. |
| Cybersecurity Mesh Architecture (CSMA) | Decentralizes security controls to enable scalable, modular, and flexible protection across assets. |
| IoT & Edge Security | Protects connected devices and data at the network edge from physical and digital threats. |
| Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) | Develops cryptographic algorithms resistant to quantum computer attacks. |
| Generative AI for Security Operations | Enhances threat analysis, response planning, and reporting using natural language and automation. |
| Advanced Email Security | Detects phishing, malware, and business email compromise with AI-enhanced filtering and sandboxing. |
| Third-Party Risk Management (TPRM) | Evaluates and mitigates risks posed by external vendors and partners with access to sensitive data |
1. AI-Driven Threat Detection & Response
AI Driven Threat Detection & Response utilizes real-time machine learning algorithms to identify anomalies in networks, endpoints, and applications. These systems improve over time as they encounter new threat attempts, thereby learning and adapting to reduce false positives and automate responses.

Empowering Security Operation Centers (SOCs) to act in seconds and not hours is a game changer in Cybersecurity. Sophisticated AI solutions from CrowdStrike and SentinelOne now support predictive analytics to foresee breaches.
Threat intelligence is contextually enhanced by AI using natural language processing and neural networks, strengthening pre-emptive posturing in intricate digital landscapes.
AI-Driven Threat Detection & Response
- Detecting anomalies in near real-time through ML algorithms.
- Automation of incident classification and operational response.
- User, endpoint, and network behavioral analytics.
- With SOAR and SIEM platforms cohesion.
- Threat intelligence and model updates continuously.
2. Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA)
In an organization’s security protocol, Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) implements the principle of, “never trust, always verify.” Each access request, regardless of where it originates, is scrutinized.
Unlike traditional, perimeter-based models, ZTA requires stringent identity verification, micro-segmentation, and enduring surveillance. ZTA is awarded as The Best in Technology for Cybersecurity because it minimizes lateral movement and insider threats in case of breaches.
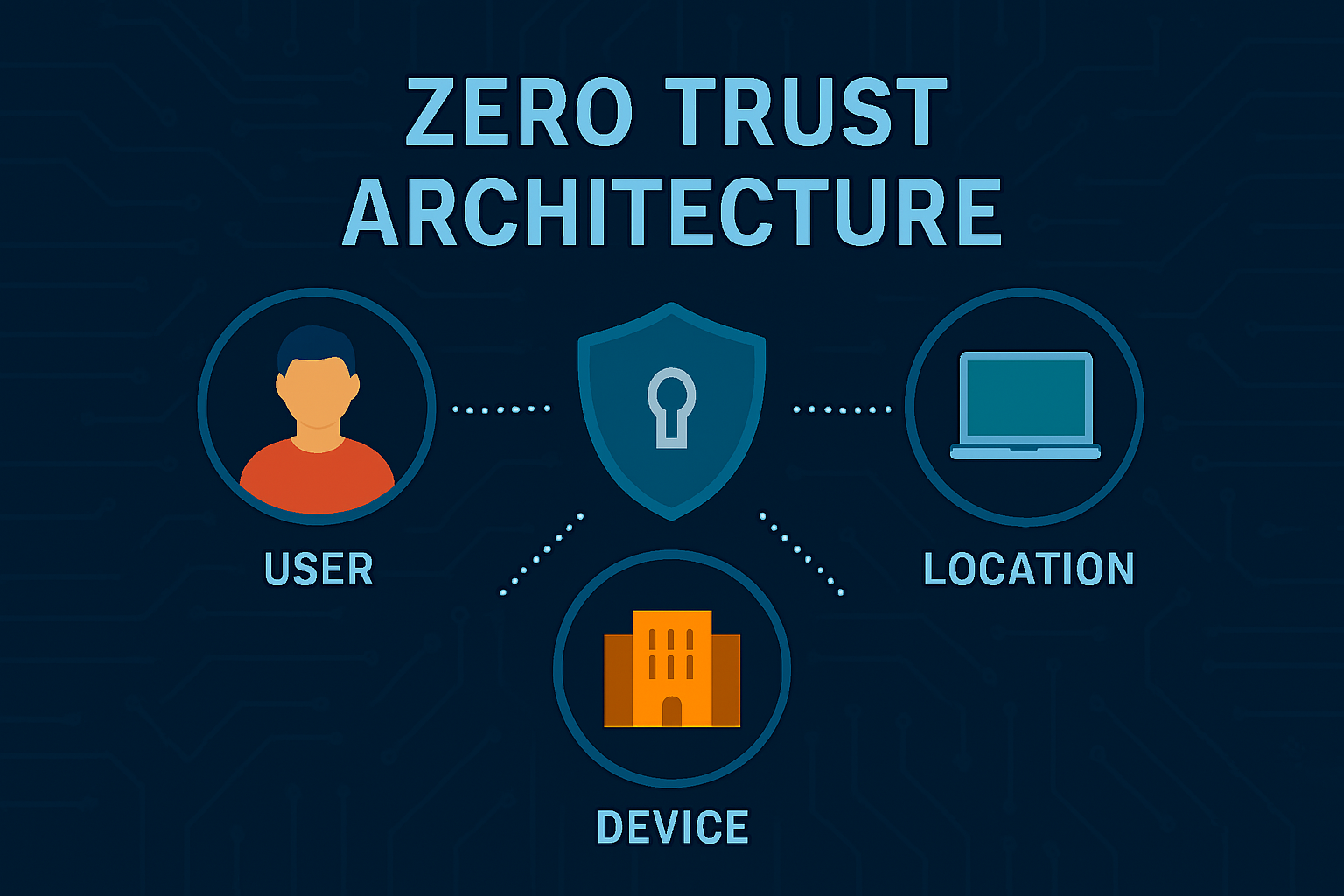
Due to remote work and BYOD trends, organizations employ ZTA frameworks coupled with IAM (Identity Access Management), endpoint security, and real-time policy enforcement and IAM tools such as Okta and Zscaler.
ZTA enforcement tools adjust security policies based on device risk and real-time behavioral evaluation, providing sensitive resource access only on a need basis.
Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA)
- Every access needs careful identity and device validation.
- Micro segmentation of applications/networks.
- Enforcement of least privilege access.
- Authentication and session monitoring.
- Works seamlessly with IAM, MFA, and endpoint security.
3. Extended Detection and Response (XDR)
XDR or Extended Detection and Response integrates endpoint, network, server, and cloud telemetry into a single workstation for comprehensive threat visibility and response automation.
Winning Best In Technology For Cybersecurity, XDR Solutions allow for faster attack signal correlation, reducing dwell time drastically. XDR, unlike traditional SIEMS, uses signal fidelity advaced analytics and MITRE ATT&CK mapping to xprioritize and neutralize real threats.

Providers like Palo Alto Cortex XDR and Trend Micro Vision One offer centralized dashboards enwith automated playbooks and behavior analytics for streamlined investigation and remediation.
XDR continues operational efficiency improvement by reducing the manual workload and increasing the automation.
Extended Detection and Response (XDR)
- Visibility over endpoints and the cloud is integrated.
- A unified interface for collecting and managing security alerts.
- Security data correlation across different layers.
- Accurate threat identification through MITRE ATT&CK mapping.
- Speedy resolution of incidents through automated incident response.
4. Cloud-Native Application Protection Platforms (CNAPP)
Cloud-Native Application Protection Platforms (CNAPP) implement protective measures for applications within multi-cloud ecosystems. They merge CSPM, CWPP, and CIEM into a single, unified structure.
CNAPPs are recognized for excellence in Technology for Cybersecurity because they offer visibility for containerized and serverless workloads, addressing vulnerabilities proactively.

Platforms like Wiz and Prisma Cloud Infra apply DevSecOps through runtime protection, configuration scanning, and automated compliance checks.
CNAPPs are also essential in a rapidly changing cloud environment, as they monitor and correct misconfigurations, privilege abuses, and secret leaks instantly.
Cloud-Native Application Protection Platforms (CNAPP)
- Security for CI/CD pipelines and production workloads.
- Features of CSPM, CWPP, and CIEM integrated.
- Serveless applications and containers are protected during runtime.
- Detection of policy violations and enforcement of misconfigurations.
- Enforcement of security policy integration for DevSecOps.
5. Cybersecurity Mesh Architecture (CSMA)
Cybersecurity Mesh Architecture (CSMA) creates a modular framework by integrating and decentralizing disparate security systems for cloud and on-premise environments. It centers on identity as the main security boundary and as such, supports real-time trust evaluation.

Best in Technology for Cybersecurity, CSMA allows shared intelligence within services for dynamic and interoperable security policies. In response to the increasing distributed IT assets, vendors such as IBM and Fortinet equip CSMA with cross-domain security frameworks, providing visibility and control.
CSMA helps companies reduce the risk of lateral attacks by creating independent, secure access points while maintaining consistent security policies.
Cybersecurity Mesh Architecture (CSMA)
- Security controls are modular and distributed.
- Enforcement of access and policies based on identity.
- Controls placed centrally while execution happens at the edges.
- Integration spanning both cloud and on-premise assets.
- Threat intelligence marked as shared across security nodes.
6. IoT & Edge Security
IoT & Edge Security is concerned with safeguarding information created and processed by edges devices like smart sensors, controllers, and autonomous systems. These devices usually do not have security features, making them easy targets for attackers.
Best in Technology for Cybersecurity, modern solutions incorporate cryptographic modules, AI-based anomaly detection, and decentralized identity frameworks.

Azure Defender for IoT and Claroty are cybersecurity solutions that provide fingerprinting and threat intelligence for IoT and cybersecurity, industrial and healthcare networks.
IoT security solutions also fortify edge devices and the transmission layer to prevent botnet attacks, data leaks, and unauthorized access and control.
IoT and Edge Security
- Fingerprinting and discovering devices.
- Booting sequences and firmware integrity checks.
- AI-based edge threat detection.
- Data encryption and strict access control.
- Remote monitoring, management, and lifecycle tracking of devices.
7. Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC)
Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) focuses on developing new encryption algorithms that would withstand attacks from quantum computers, which are predicted to decrypt current RSA and ECC cryptography.
Best in Technology for Cybersecurity, PQC safeguards critical information for the projected era of quantum computing. NIST is developing benchmark quantum-resistant algorithms, with preliminary implementations from PQC, IBM, and Google.
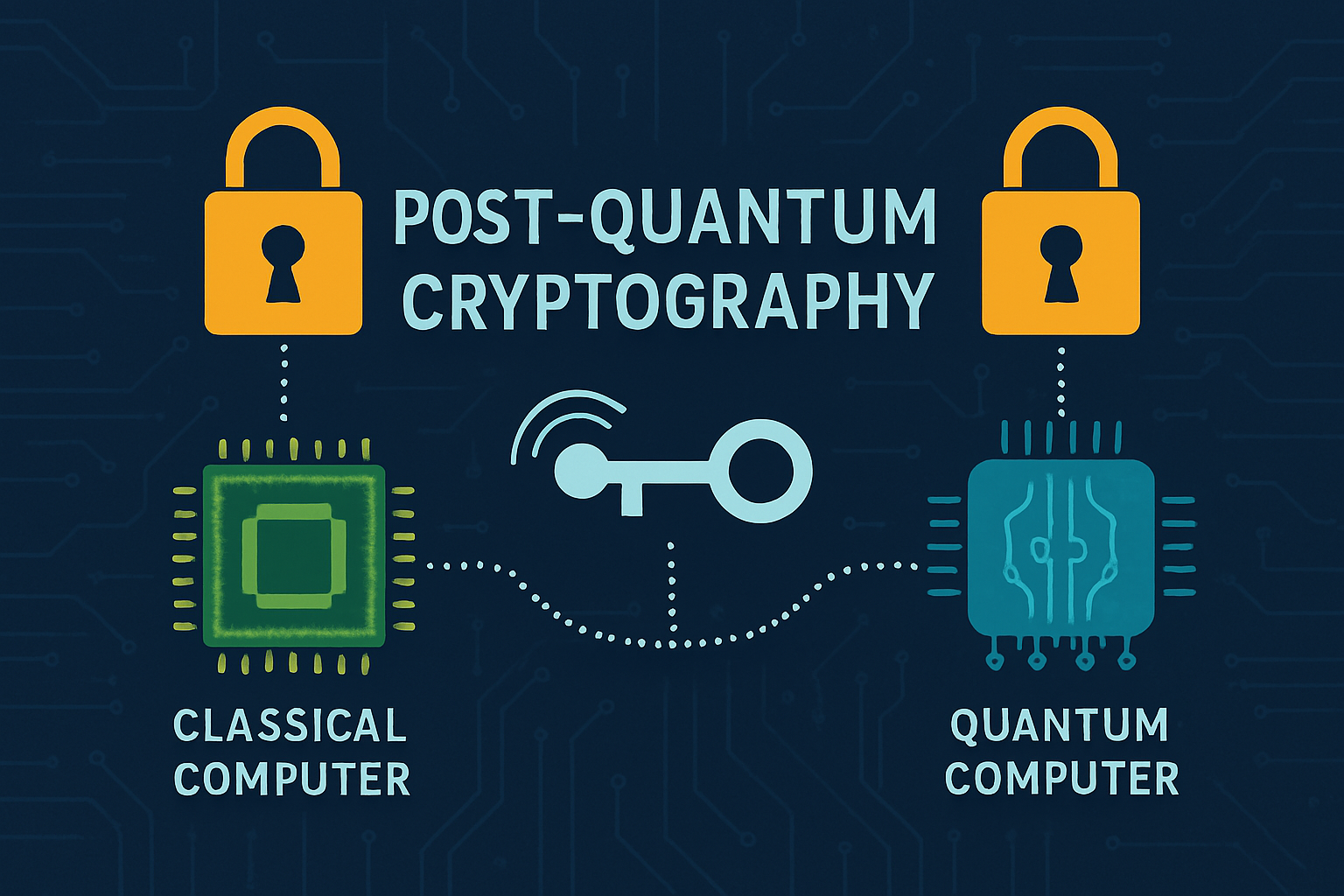
PQC combines lattice-based and hash-based methods, integrating them into hybrid cryptographic frameworks to enable backward compatibility.
The shift towards quantum computing is happening quickly, and transitioning to PQC now will fortify digital resources from quantum decryption.
Post-Quantum Cryptography
- Quantum resistant algorithms.
- Cryptography using lattices, codes, and hashes.
- Transitional compatible hybrid encryption frameworks.
- Enterprises can adopt it once standardized by NIST.
- Guarantees confidentiality of sensitive data for extended periods.
8. Generative AI for Security Operations
Generative AI is changing the landscape for security operations by streamlining the processes for threat detection, alert triage, and resolution workflows.
On top of these, AI models are capable of summarizing logs, creating incident reports, and even running simulations of prospective future scenarios for better preparedness.

While they may be considered the best in technology for cybersecurity, generative AI further supplements the efforts of human analysts by offering conversational insights and context relevant to datasets which is far beyond the traditional cybersecurity data analyzer.
Subtle attack pattern recognition and creating defenses against them is done by Microsoft Security Copilot and Google Chronicle, which leverages large language models to do so.
There is now an improvement for firms in the SOAR (Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response) Platforms through generative AI, which in turn also helps in decision ecosystem and agility in the face of persistent advanced sophisticated threats.
Security Operations Utilizing Generative AI
- Threat and incident report automation.
- Security log and alert evaluation using NLP.
- Simulation of potential attacks by AI.
- Predictive analytics within SOAR and SIEM through AI models.
- Contextual alerting and foresight analytics explanation.
9. Advanced Email Security
Advanced Email Security is powered to combat new age threats such as spear phishing, credential harvesting, and emails which have the capability to extract ransomware.
Award winning solutions for cyber security shows us that AI is now capable of discerning the tone of a sender, their metadata, and even their behavior as far as sender content and sender behavior for malicious intention as proof of the next level in technology.

Through natural language processing and a behavioral baseline, proofpoint and abnormal security can cite suspicious mails and even communications beyond email. URL and sandbox rewriting fortifies these systems.
There is also DMARC enforcement, phishing simulation in real time, and integrated training for employees which with all these features make these systems preferable and fortifies the email, which is considered as the weakest element in an enterprise, even stronger.
Email Security
- Phishing and malware detection using AI.
- Senders and content of emails are scrutinized for behavioral patterns.
- Dynamic URL rewriting and sandboxing.
- Enforcement of DMARC, DKIM, and SPF protocols.
- Protects against spoofing and business email compromise.
10. Third Party Risk Management (TPRM)
Third Party Risk Management (TPRM) focuses on assessing and minimizing security risks from suppliers, associates, and other contractors who have the potential to compromise internal systems or data.
With a growing number of cyber supply chain threats, the TPRM PR vigilant and Security Scorecard platforms are offering breach notification, real-time risk scoring, and compliance tracking. These platforms are the Best in Technology for Cybersecurity.

Automated compliance checks and continuous observation of vendor ecosystem compliance and onboarding risk assessment are among the features of advanced TPRM systems.
Enterprises require advanced TPRM systems in order to discover the attack surfaces and to ensure all external relations abide to the security standards of the organization without hindering organizational agility.
Third-Party Risk Management
- Continuous vendor security posture monitoring.
- Automated assessment and monitoring of risk.
- Vendor evaluation and compliance monitoring.
- Instant notifications for third-party security incidents.
- Managed security obligations compliance and audit trails.
Conclusion
The Best in Technology for Cybersecurity protects vital assets from advanced threats by utilizing automation, intelligence, and flexibility. Every innovation from AI-Driven Threat Detection and Response to Zero Trust Architecture and Post-Quantum Cryptography contribute to securing modern infrastructures.
As cyber risks become more complex, frameworks such as XDR, CNAPP, and CSMA provide integrated holistic visibility and resilience. At the same time, other generative AI, IoT security, and third-party risk management enhance security across diverse environments.
These technologies boost cybersecurity strategies across all industries, making the technologies vital to embrace for the future.









