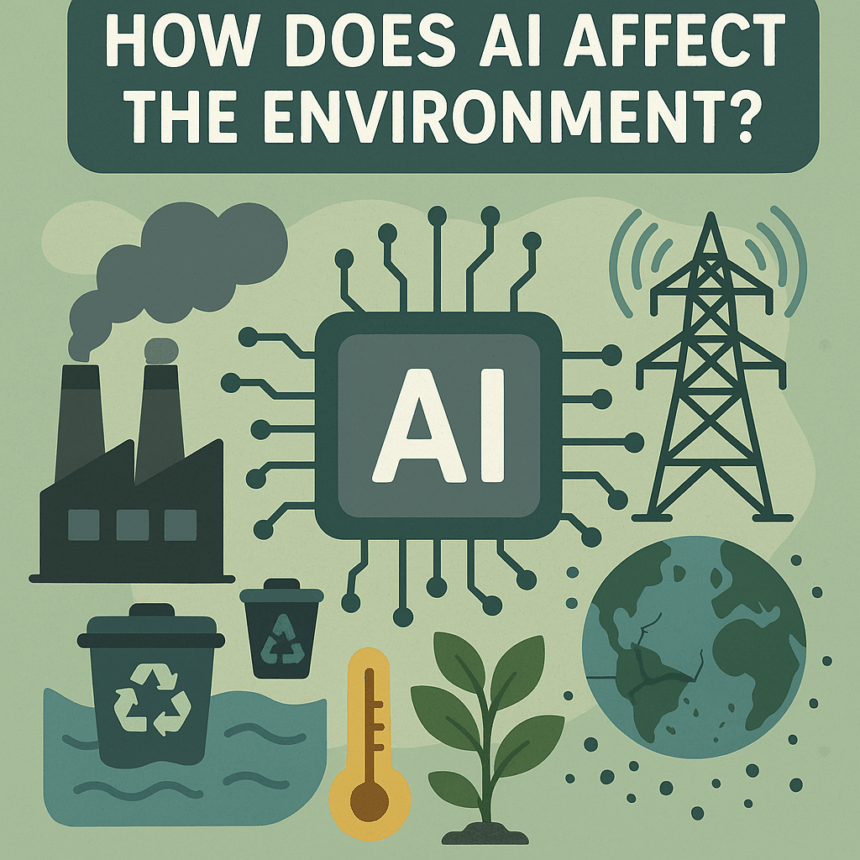
In this article, I will cover the How Does AI Affect the Environment by discussing both sides. Though Artificial Intelligence (AI) technology has the potential to reshape industries for the better, it also comes with a set of problematic considerations.
With AI’s advanced surge in usage, there are emerging concerns on its energy consumption as well as its ability to serve as an effective instrument for monitoring climate changes.
What is AI Environment?
An AI environment is the context where an artificial intelligence system works, learns, and makes decisions. It contains data repositories, algorithms, integration systems including sensors, user inputs and feedback loops to aid interaction of the systems with their environment.
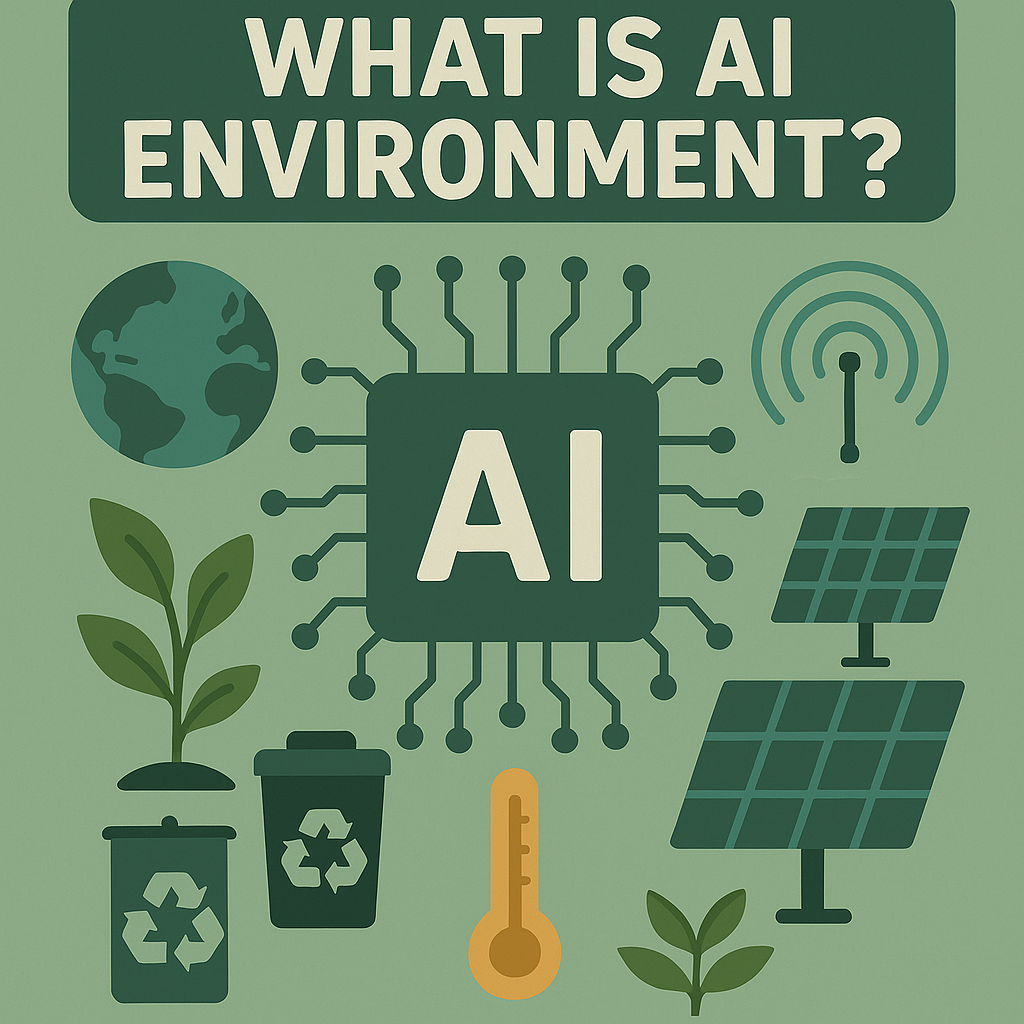
The AI environments can either be a virtual space such as a simulation or real world examples like smart homes or self-driving cars. A certain AI environment determines how the system will learn, adapt and respond in different situations.
How Does AI Affect the Environment?
AI comes with both pros and cons when it comes to environmental preservation. Although some may claim this 100% accurate breakdown is difficult to understand, allow me to present it in easier steps:
Energy Consumption
There’s A LOT of computing going on over at large AI models. The most relevant part to the environment is that their training requires a lot of electricity because of the usage of fossil fuels.
Data Center Impact
AI needs data centers as its core oxygen, and those have a tendency to use up a ton of combustibles while generating heat.
E-Waste Generation
Systems with frequent AI updates give rise the need for new hardware which increases electronic waste.
Environmental Monitoring
The use of satellites together with predictive modeling enables AI also has deforestation tracking abilities alongside pollution as well as climate
Resource Optimization
On the positive side fulfillment of energy efficiency in industries sharp drop towards agriculture makes room branches and
The bottom line is that Ai has streaming capabilities through resource applications but at the same time maintains powerful features aimed towards protection and sustainable economic growth.
Benefits of AI on the Environment
Anticipating and Tracking Natural Disasters
AI tools can process large quantities of data to track weather patters, model climate change, predict natural disasters, and aid governments in refining their responses.
Reducing Energy Waste
AI helps make buildings smarter by controlling power usage in factories and smart grids, leading to a reduction of unnecessary power consumption.
Safeguarding Endangered Species
Conservation drones equipped with artificial intelligence can monitor wildlife and detect poaching activities in real-time.
Controlling Environmental Pollution
Using sensors and satellites, AI is able to monitor both air and water pollution, taking action as needed when harmful emissions are detected.
Improving Agricultural Practices
With the help of AI technology, farmers are now able to use water more efficiently along with other resources such as fertilizers and pesticides
How AI Negatively Impacts Nature
Reduction In Lifespan Of Hardware – With the constant rise in new innovations such as Apparent AI, devices tend to be discarded at a faster pace than they should leading to an increase waste pile coupled with more material extraction adversity for new components.
Electricity Waste – The training and operation of significant AI algorithms involve extensive computer power, resulting in high energy consumption and additional carbon emission.
Creation of E-Waste – Legacy hardware which gets obsolete because of the upgradation in AI tends to escalate electronic waste which is hazardous if proper recycling techniques are not employed.
Data Hubs Carbon Footprint – Operations that deal with Artificial Intelligence have data centers that rely on fossil fuels for their energy, hence contributing toward pollution that causes global warming.
Manufacturing Requirements Put a Natural Strain – Striking new technology requires new an improved artificially intelligent chips and machinery which entails more advanced equipment and thus depletes natural resources.
Ethical and Policy Considerations
Energy Transparency – Developers must publicly share their energy consumption as well as the impact on the environment while training their AI models for model accountability and sustainability.
Equitable Access – With a goal to bridge inequality gaps, Environmental AI tools should not be restricted by geography, especially in underdeveloped countries.
Regulation and Standards – Policymakers have to put in place regulations that deal with AI energy efficiency e.g. setting minimum standards for e-waste as well as environmental regulations on AI use.
Responsible Innovation – Ethical innovation focuses equally on social responsibility which means caring for the environment, making sure that there is support on ecology friendly goals in any AI innovations done.
Bias and Fairness – Environmental AIs are to uphold data integrity concerning biases ensuring all participants racially diverse communities involving even nature are treated equally without discrimination.
Conclusion
AI has a double-edged impact on the environment; it can either assist or hinder. The creation and use of AI systems typically require a lot of energy and produce e-waste, but at the same time, AI can greatly assist in monitoring changes to the climate, pollution levels, and resource management.
In order to sustain our future, we must practice responsible innovation while protecting our natural resources along with adopting ethical practices in artificial intelligence.