In the following article, I will discuss the Top Secure Crypto Bridges to Avoid Hacks where I will focus on secure platforms for transferring assets between blockchains.
Ensuring the security of transactions is fundamental with rising cross-chain activities to mitigate risk exposure.
I will analyze the protective features and security protocols implemented by each of these crypto bridges within the discussed limitations.
Top Secure Crypto Bridges to Avoid Hacks & Key Point
| Bridge | Key Point |
|---|---|
| LayerZero | Omnichain messaging with Ultra Light Nodes for minimal trust and high security. |
| Synapse Protocol | Optimistic verification model with secure liquidity pools for fast cross-chain swaps. |
| Axelar Network | Decentralized PoS validators ensuring secure cross-chain communication. |
| Wormhole (post-recovery) | Enhanced guardian upgrades and constant auditing after 2022 hack recovery. |
| Celer cBridge | State Guardian Network (SGN) ensures safe, decentralized asset transfers. |
| Hop Protocol | Rollup-focused bridge using liquidity pools to avoid custodial risks. |
| Chainlink CCIP | Cross-chain messaging secured by decentralized Chainlink oracle networks. |
| Connext | Non-custodial, trust-minimized architecture relying on liquidity routers. |
| deBridge | Decentralized validation and strong open-source audit-first approach. |
| Across Protocol | Optimistic relayer system with dispute mechanisms for secure transfers. |
1. LayerZero
LayerZero is an interoperability protocol in blockchain technology which aims to facilitate communication between blockchains in a trustless and secure manner without any third parties involved.
The security of LayerZero relies on Ultra Light Nodes (ULNs), which is a type of blockchain node that significantly reduces the computational resources needed to verify messages between blockchains, cross-chain message verification, compared to traditional full nodes.

Because of this, LayerZero makes use of decentralized validator networks along with independent oracles (i.e. Chainlink, Band Protocol) who guarantee message validation with minimal centralization.
By splitting the functions of oracles and relays, LayerZero eliminates single points of failure which greatly enhances its resistance to exploits. T
he protocol has yet to face significant hacks, and its security as a bridge is strengthened due to regular audits of the open-source codebase. However, users need to be cautious about validators’ sets being too centralized as it can lead to potential risks.
LayerZero Features
- Omnichain Communication: Enables seamless cross-chain communicating throughout different platforms.
- Ultra Light Nodes (ULNs): Secures cross-chain transactions using nodes with minimal resources.
- Centrally Managed Security: Uses oracles and relayers as validators which create a more decentralized approach.
2. Synapse Protocol
Synapse Protocol is an interoperability network with cross-chain asset transfer and messaging capabilities that focuses on security and scalability. It operates on optimistic verification model—transactions are assumed valid by default until challenged within a dispute duration, which minimizes the chances of fraudulent transfers.
Synapse’s liquidity model makes safety payments by using liquidity pools that are decentralized, reducing the economic consequences of possible hacks by distributing assets across many chains.
Also, the protocol’s bridge contracts undergo continuous audits and its security has been improved after some minor issues in its earlier days (pre-2023). Such a hybrid mix of optimistic security and stringent liquidity provisions offers dependability for cross-chain transfer.
However, as with the optimistic model, the proactive measures to submit timely required fraud proofs can be burdensome to user in higher latency environments.
Synapse Protocol Features
- Optimistic Verification: Adds a marginally higher chance for fraud to verify transactions.
- Liquidity Pools: Make asset exchanges easier and more secure while removing the need for centralized custody.
- Multi-Chain Expansion: Operates on multiple blockchains, improving cross-chain interactions.
3. Axelar Network
The Axelar Network solves the problems of cross-chain communication using a decentralized approach, allowing the transfer of assets and messages through a proof-of-stake (PoS) mechanism.
Its independent validator nodes guarantee that there is no single point of authority that cross-chain transactions are validated, which greatly minimizes the potential for hacks.

Axelar uses end-to-end cryptographic security, meaning that messages are encrypted and verified at both the source and destination chains, which further secures the process during transit.
The protocol’s modifiable structure permits add-ons from Ethereum and other blockchains Cosoms, preserving the overall system’s integrity. Axelar has not suffered major exploits, maintaining an exemplary security record due to regular audits, transparent governance.
Reliance on verifying the diversity of participants in the PoS system is a major concern for security, meaning users have to trust that the network of Axelar validators is decentralized enough.
Axelar Network Features
- Distributed Validator Set: High security with additional distributed validators for extra.
- Proof of Stake Verification: Validates transactions through a protected PoS model.
- Cryptographic Shield: Users’ assets are secured using end-to-end cryptographic techniques.
4. Wormhole
After the guardian network hack that Wormhole sustained, cross-chain messaging was brought to the limelight. Multi-chain ecosystems support communication between blockchains and cryptocurrencies, and this incurs the risk of a vulnerability.
The consequence is devastating as was highlighted in the incident where more than 300 million USD was lost. Post recovery, Wormhole have made improvements cyber security developments that enable it to stand out in the gap as one of the leading secured bridges in the current market.

Enhanced post recovery features include: real-time extremes, monitoring, anomaly identification, unauthorized transaction prevention, and cross-chain message validation which minimizes single point of failure risks.
Restoration of faith was enabled through the open posting of security measure implemented resulted due to no untoward incident reported after implantation. Unlike other protocols where roadmap relies on promise, this one relies on trust, and proactively spearheading progressed control, act along with the open commitment mold of the protocol during deployment.
However, upon execution it is paramount for users along with the public worm signs the past vulnerability highlighted the unfulfilled gap results constant shield improvement highlighted as Paradox deployed security blank.”
Wormhole Features
- Guardian Network: Decentralized group of guardians who stops maleficent validation of transactions.
- Continuous Auditing: Regular audits and security checks are sustained for safety.
- Building Network Security: Fixing exposed weak spots after the 2022 hack enhancing system security
5. Celer cBridge
A division of Celer, cBridge is a cross-chain asset transfer protocol that utilizes State Guardian Network (SGN) for bridging secureness and efficiency. The SGN is a decentralized validator network that watches over and confirms cross-chain transactions using a blend of cryptographic proofs and state channel user verifiability.
This hybrid security model enables cBridge to optimize decentralization and low-latency transfer suitable for high throughput applications. Celer’s design reduces trust assumption by allowing users to independently verify transaction validity without depending on SGN.
This system provides good hack resistance with no major breaches noted and its open-source code base is under audit. Still, the effectiveness of SGN relies on the level of decentralization and trustworthiness of its validators; as such, users must scrutinize the network’s makeup for adequate security.
Celer cBridge
- State Guardian Network (SGN): Protecting the cross-chain transaction process is administered by decentralized validators for celer network.
- Trust-Minimized Architecture: Designed so that funds aren’t under the custodianship of a singular party.
- Cross-Chain Liquidity: Transferring funds between chains without the risks of custody is made easier.
6. HOP PROTOCOL
Hop Protocol is a dedicated roller-to-roller transfer bridge within the Ethereum layer-2 ecosystem. Unlike bridges that lock and then mint assets, Hop uses liquidity pools and AMMs to transfer assets across chains without custodial intermediaries, singular points of failure, or centralization.
This design reduces the risks of unexploitable access to locked assets collateralized funds, as they are held by decentralized liquidity providers. Rollup-centric design guarantees compatibility with scalable layer-2s like Optimism and Arbitrum, reinforcing security and efficacy.
The protocol has not suffered any significant hacks and offers a reliable option due to its secured simplicity and transparency. However, system based on liquidity pools incur the risk of impermanent loss, though this is a financial, not security, issue.
Hop Protocol Features
- Liquidity Pools: Streamlines transfer of assets on all Ethereum layer 2s.
- No Custodial Risk: The risk of centralized custodianship is avoided by utilizing liquidity pools instead of lock-and-mint systems.
- Fast Settlements: Compared to traditional cross-chain bridges, transfer of assets is done more quickly.
7. Chainlink CCIP
Chainlink’s CCIP is a cross-chain messaging protocol built on top of Chainlink’s ecosystem, incorporating its decentralized oracles for secure cross-chain interoperability. CCIP supports a blockchain-wide oracle network for message validation and relaying within blockchains and maintains security and privacy through cryptographic sealing.

Its Risk Management Network monitors transactions for malicious actions and allows for immediate intervention to stop suspicious transactions. CCIP is integrated with the Chainlink infrastructure used to secure billions worth of assets in DeFi, making it one of the most powerful bridges available.
It has no reported exploits, which, combined with its extensive audit history and open documentation, enhances trust. The weakness in the system relies on all oracles being replaced; while CCIP has strong decentralization, continued surveillance is necessary to ensure their reliability.
Chainlink CCIP Features
- Cross-Chain Messaging: Transfer of messages from one blockchain to another is done in a secure manner.
- Decentralized Oracle Network: Chainlink’s trusted oracle scaffold is made use of for validation.
- Anti-Fraud Detection: Fraudulent activity in any cross-chain operations are detected and prevented through built mechanisms.
8. Connext
Cross-chain transfers are securely enabled by Connext, which operates as a non-custodial, trust-minimized bridge. Briges lack security, which is why user assets are never taken custody of. Instead, transfers are done through decentralized routers, meaning no hacks can occur.
Users have full control of their assets during every step of the transfer, meaning no custody is needed. This liquid hop system guarantees security via state channels and cryptographic mechanisms.
As such, the design of Connext is optimal for fast and cost efficient transfers for layer 2 networks, EVM compatible chains, and other supporting architectures. In addition, Connext has never been put in the news for any major exploits, meaning their security is clean.
Being regularly audited boosts the security of the openly sourced codebase. Regardless of this, the Connext router network remains dependent on the providers for their liquidity and honesty. That being said, users must be on the lookout to verify this information.
Connext Features
- Non-Custodial Design: Users retain control of their funds at all time.
- Liquidity Routing: Assets are routed through a network of decentralized liquidity providers.
- Verifiable Proofs: Transparent transactions are conducted through the use of cryptographic proofs.
9: deBridge
Reinforcing security using a validator-operator model and open-source visibility, deBridge is a cross-chain bridge with a difference. No single validator centralizes control over the bridging process as cross-chain transactions are validated by a host of independent validators.
Through extensive third-party audits and a bug bounty program, which rewards the identification of exploits, the security infrastructure of deBridge is greatly bolstered. Its code can be accessed freely, enabling community implementation scrutiny which helps foster trust.

Andue to the focus on decentralization and transparency, it is still difficult to breach and no major hacks have been documented.
While the longevity of the system concerning security usage audit trails is adaptable, the underlying design principles are anti-hack mechanisms strengthened deBridge’s framework.
deBridge Features
- Decentralized Validators: A group of validators who sign the transactions are relied upon. This reduces the risk of centralised attacks.
- Open-Source Transparency: The code is open-sourced which allows people to identify security flaws rapidly and fix them.
- Regular Audits: Maintains a considerable level of protection through ongoing security audits.
10. Across Protocol
With the use of relayer systems, Across Protocol functions as a cross-chain bridge that allows users to transfer their assets safely and quickly. An optimistic security model is used, where transactions are assumed to be valid until there is a dispute within a predefined timeframe with a strong mechanism in place to deal with possible fraud.
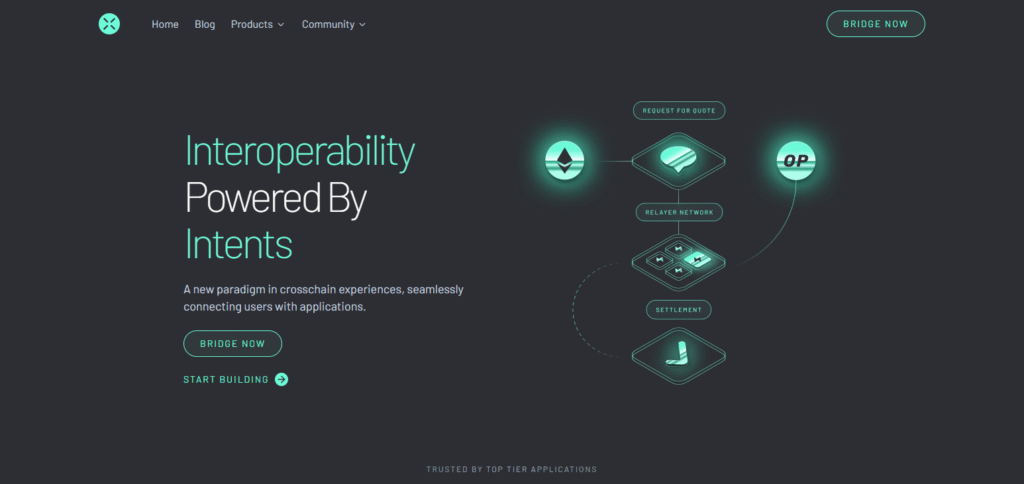
Relayers of Across are funded to be honest which helps the protocol’s design minimize trust assumptions by enabling the users to verify the transactions. Moreover, the protocol’s design and focus on speed and cost-efficiency makes it popular for bridging across Ethereum layer-2, while also maintaining security.
There have been no major hacks with Across, and the transparent governance along with regular audits increase reliability. But, users have to monitor such systems closely to ensure prompt fraud-proof submission, making optimistic systems active surveillance systems.
Across Protocol Features
- Relayer System: Based on relayers, a novel approach guarantees the safe cross-chain transfer of assets.
- Dispute Mechanism: Assigned an optimistic approach, disputes resolution handles erroneous transactions.
- Trust-Minimized: Dependence on trust is lowered with the use of distributed validators and relayers.
Conclusion
Protecting cross-chain transactions from hacks and safeguarding user assets in the quickly evolving domain of blockchain technology is crucial. The Top Secure Crypto Bridges to Avoid Hacks provides strong protection using trust minimized architectures, sophisticated cryptography, and decentralized validation.
These bridges enable users to securely and reliably transfer assets across blockchains through decentralized validators, liquidity pools, and continuous auditing.
Chainlink’s oracle network and LayerZero’s lightweight nodes, for instance, are protected bridges that ensure secure transfers of digital assets regardless of the employing technology. Amid the expanding landscape of blockchain ecosystems, these secure bridges serve as important cross-chain interoperability infrastructures.










