In this article, I will cover Unusual Alternatives to NFTs for Proving Digital Ownership. These methods surpass NFTs in more ways than one, offering verification and management methods of ownership through soulbound tokens, smart contract licensing, and decentralized identities.
These methods are more reliable and flexible in proving ownership of digital assets in emerging blockchain environments.
Key Point & Unusual Alternatives to NFTs for Proving Digital Ownership List
| Token/Technology | Keypoint Summary |
|---|---|
| Soulbound Tokens (SBTs) | Non-transferable tokens representing personal identity or credentials. |
| Smart Contract Licensing | Automates licensing agreements and enforces terms on blockchain. |
| Digital Twin Tokens | Tokenized digital replicas of physical assets for tracking & proof. |
| Time-Locked Access Tokens | Tokens granting access only after a predetermined time period. |
| Metaverse Land Tokens | Digital ownership tokens for virtual real estate in metaverse worlds. |
| Encrypted QR Ownership Tags | Secure QR codes encoding ownership data for asset verification. |
| Decentralized Identity (DID) | Blockchain-based user identity management without central control. |
1.Soulbound Tokens (SBTs)
Soulbound Tokens (SBTs) mark a departure from the norm of NFTs, as Pertaining to NFTs, while they are usually purchasable and transferable, SBTs are linked to a single digital persona indefinitely, making them non-transferable and non-tradable.

Their inability to be traded or transferred makes them most suitable for ascertaining a person’s credentials, reputation, or ownership. Their non-transferability challenges the traditional ownership model, making SBTs a distinct way to establish verifiable digital ownership without market speculation.
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Nature | Non-transferable tokens permanently bound to a single digital identity |
| Purpose | Prove personal credentials, reputation, or ownership tied directly to an individual |
| KYC Requirements | Minimal or no KYC needed as ownership is identity-linked, reducing friction and privacy |
| Transferability | Cannot be sold, gifted, or transferred, ensuring authentic and unique ownership |
| Use Cases | Digital certificates, memberships, licenses, reputation systems |
| Security | Enhanced trust through blockchain immutability and identity-binding |
| Advantages | Prevents speculation, forgery, and fake ownership claims |
| Limitations | Less liquidity compared to traditional NFTs due to non-transferability |
2.Smart Contract Licensing
Smart Contract Licensing provides an atypical substitution to NFTs for documenting digital ownership since it seeks to automate and enforce rights through programmable contracts instead of depicting ownership as a mere static representation.
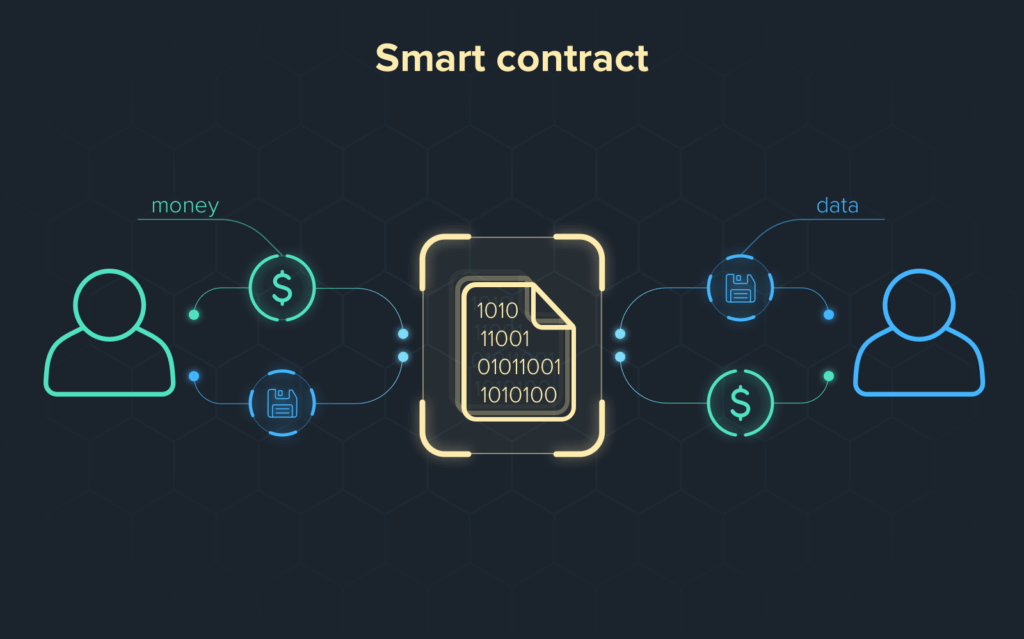
Unlike NFTs primarily meant for proof of ownership, smart contract licensing establishes active mechanisms with rules and limitations of use as well as automatic payment of fees, royalties to the owners within the transfer of ownership process.
This advancement makes ownership more unrestricted and more precise than before whereby the digital assets of the creators and owners are governed in real time and could be controlled in regard to their usage, transfer, or monetization and flooding the market with NFTs no longer serves the purpose.
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Nature | Automated, programmable contracts that govern licensing and ownership terms |
| Purpose | Enforce usage rights, royalties, and conditions directly through blockchain code |
| KYC Requirements | Minimal KYC since ownership verification relies on contract logic, not identity checks |
| Transferability | Ownership can be conditional and controlled dynamically via contract rules |
| Use Cases | Software licenses, digital content rights, subscriptions, royalty distribution |
| Security | Immutable and transparent contract terms ensure compliance and reduce disputes |
| Advantages | Flexible control over asset use, automatic royalty payments, no need for middlemen |
| Limitations | Requires technical setup and understanding of smart contracts |
3.Digital Twin Tokens
Digital Twin Tokens serve as a fascinating substitute for NFTs in asserting digital ownership, as they replicate tangible assets monolithically on the blockchain, fractionalizing bridges between the physical and digital realms.

Unlike NFTs, which merely embody digital creations, these tokens associate with physical objects, allowing for accurate tracking and verification of the assets. This novel fusion enables a more practical verification of ownership, especially in cases where authenticity and condition surveillance involves more than a digital representation.
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Nature | Digital replicas of physical assets represented on the blockchain |
| Purpose | Link digital ownership directly to real-world objects for authenticity and tracking |
| KYC Requirements | Minimal KYC as ownership ties to asset verification rather than personal identity |
| Transferability | Transferable tokens reflecting changes in ownership of the physical asset |
| Use Cases | Real estate, luxury goods, machinery, collectibles with physical counterparts |
| Security | Combines blockchain immutability with real-world asset verification methods |
| Advantages | Bridges physical and digital worlds, enhances trust and provenance |
| Limitations | Requires reliable real-world data feeds and verification mechanisms |
4.Time-Locked Access Tokens
Time-Locked Access Tokens provide a unique way of verifying digital ownership, distinguishing them from NFTs by managing when access to a digital asset can be granted. Whereas NFTs are traditionally designed to provide instant and irrevocable ownership, these tokens grant access only when a particular date arrives or a condition is met.
This method of ownership adds control and much more security. Ideal for controlled access in subscriptions or staged release in content access in the digital realm, ownership shifts from possession to possession with conditional access
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Nature | Tokens that grant access or ownership rights only after a predetermined time or condition |
| Purpose | Control timed or conditional access to digital assets |
| KYC Requirements | Minimal KYC since ownership is linked to token holding and timing, not personal identity |
| Transferability | Transferable but access activates only after time-lock conditions are met |
| Use Cases | Limited releases, subscriptions, event tickets, phased content delivery |
| Security | Time-lock enforced by smart contracts ensuring strict access control |
| Advantages | Adds exclusivity and control over when ownership benefits can be exercised |
| Limitations | Access delay may reduce immediate usability or liquidity |
5.Metaverse Land Tokens
Tokens for Metaverse Land are different from NFTs since they confer ownership of virtual property within fully-fledged digital worlds as opposed to artworks or collections. Unlike NFTs, these tokens bestow the rights to build upon, trade, or profit from different sections of virtual land, thus, ownership is blended with actual utility and social engagement.

The active interaction with an evolving environment is what makes Metaverse Land Tokens distinguishing as a means of proving digital ownership surpassing static assets to transform virtual spaces into prized functional properties.
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Nature | Tokens representing ownership of virtual real estate within metaverse environments |
| Purpose | Prove and manage rights to digital land parcels for building, trading, and monetization |
| KYC Requirements | Minimal KYC as ownership is linked to token wallets rather than personal identity |
| Transferability | Fully transferable tokens enabling buying, selling, and leasing of virtual land |
| Use Cases | Virtual property development, gaming, social hubs, digital commerce spaces |
| Security | Blockchain ensures transparent ownership and protection against fraud |
| Advantages | Combines digital ownership with active utility and social interaction |
| Limitations | Value depends on metaverse platform popularity and user engagement |
6.Encrypted QR Ownership Tags
Encrypted QR Ownership Tags offer a unique substitute to NFTs through scannable codes that provide proof of ownership digitally in a straightforward, yet secure manner. Unlike NFTs which are logged on blockchain platforms, ownership tags attach encrypted data to the item itself which can be scanned for immediate verification.

This approach seamlessly integrates offline and online verification, making it useful for tangible assets or digital items that require immediate, secure proof of ownership and cannot solely depend on blockchain marketplaces or wallets.
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Nature | QR codes embedding encrypted ownership data for secure and quick verification |
| Purpose | Provide tamper-resistant proof of ownership for physical or digital assets |
| KYC Requirements | Minimal KYC as verification relies on encrypted data, not personal identity |
| Transferability | Ownership can be transferred by updating encrypted data linked to the QR code |
| Use Cases | Product authentication, event tickets, digital certificates, asset tracking |
| Security | Encryption ensures data integrity and prevents forgery during scanning |
| Advantages | Combines offline and online verification, easy to use without complex blockchain setup |
| Limitations | Dependent on secure encryption methods and physical tag integrity |
7.Decentralized Identity (DID)
Decentralized Identity (DID) offers a unique and untraditional alternative to NFTs for verifying digital ownership as it seeks to empower the individual to govern their own identity without the aid of a central body. Unlike NFTs which primarily act as a proxy for digital assets, DIDs allow people to control verified certificates and personal information on different platforms.
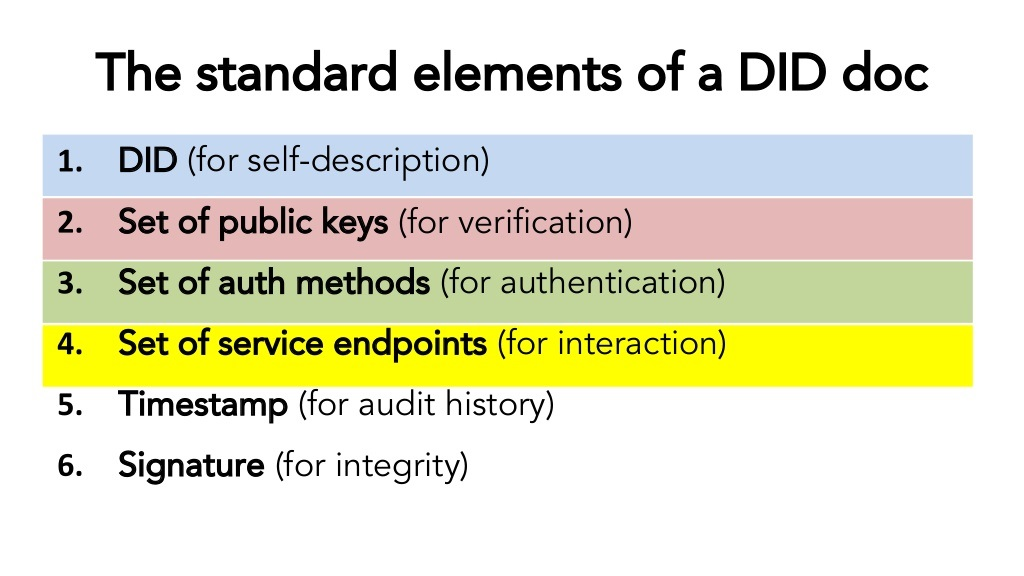
This approach of self-sovereignty moves the focus of ownership from assets to identity which bestows a trust anchor and authentication that can facilitate digital ownership while safeguarding privacy.
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Nature | Blockchain-based self-sovereign identity system controlled by the individual |
| Purpose | Enable secure, private, and verifiable ownership of identity and credentials |
| KYC Requirements | Minimal KYC as users manage their own identity data without centralized authority |
| Transferability | Identities are non-transferable, bound to the individual |
| Use Cases | Digital identity verification, credential management, access control |
| Security | Cryptographic proofs and blockchain immutability protect against identity fraud |
| Advantages | Enhances privacy, user control, and interoperability across platforms |
| Limitations | Adoption depends on ecosystem support and user understanding |
Conclusion
Innovative methods such as non-transferable ownership, programmable licenses, linking to physical assets, timed or timed access, virtual property rights, encrypted verification, and self-sovereign identity create more nuanced and rigorously defined boundaries around digital ownership as compared to NFTs.
The range of these mechanisms enhances the functionality of digital ownership to establish control, verification, and management, addressing NFTs shortcoming while augmenting precisions and looser configurability.
FAQ
What makes these alternatives “unusual” compared to traditional NFTs?
These alternatives differ by focusing on non-transferability, real-world asset integration, programmable rules, timed access, or decentralized identity management, offering more specialized and practical ownership proofs beyond simple digital collectibles.
How do Soulbound Tokens (SBTs) differ from NFTs?
SBTs are non-transferable and permanently linked to an individual’s identity, making them ideal for credentials or reputation, unlike NFTs which are typically tradeable.
What is Smart Contract Licensing?
It uses programmable contracts to automate and enforce ownership terms like usage rights and royalties, allowing dynamic control rather than just static proof of ownership.