In this article I will explain Difference Between Blockchain and DAG, two emerging technologies for capturing digital transactions differ from each other.
Although both strive for the same goal of providing a secure and decentralized system, both are structurally different and vary in terms of speed, scalability, and uses.
Knowing these differences is important when selecting the suitable technology for applications such as cryptocurrencies, IoT, and smart contracts.
What is Blockchain?
A blockchain is a secure, clear, and incorruptible record of transactions kept on a virtual ledger that is distributed across a network of computers. A record of transactions are placed in a block, and these blocks are interlinked to form a chain in a sequential manner.
Data in a block cannot be changed without changing the entire successive blocks which needs agreement from the network; hence data in blocks is immutable.
Because of the above reason, blockchain technology is very useful in scenarios where trust, clarity, and security are required like in cryptocurrencies, managing the supply chain of products, secure self-executing contracts.
What Is DAG?
DAG is known as a Directed Acyclic Graph. A data structure that occurs in the field of computer science is used to represent a collection of a set of objects connected by edges which are directed.
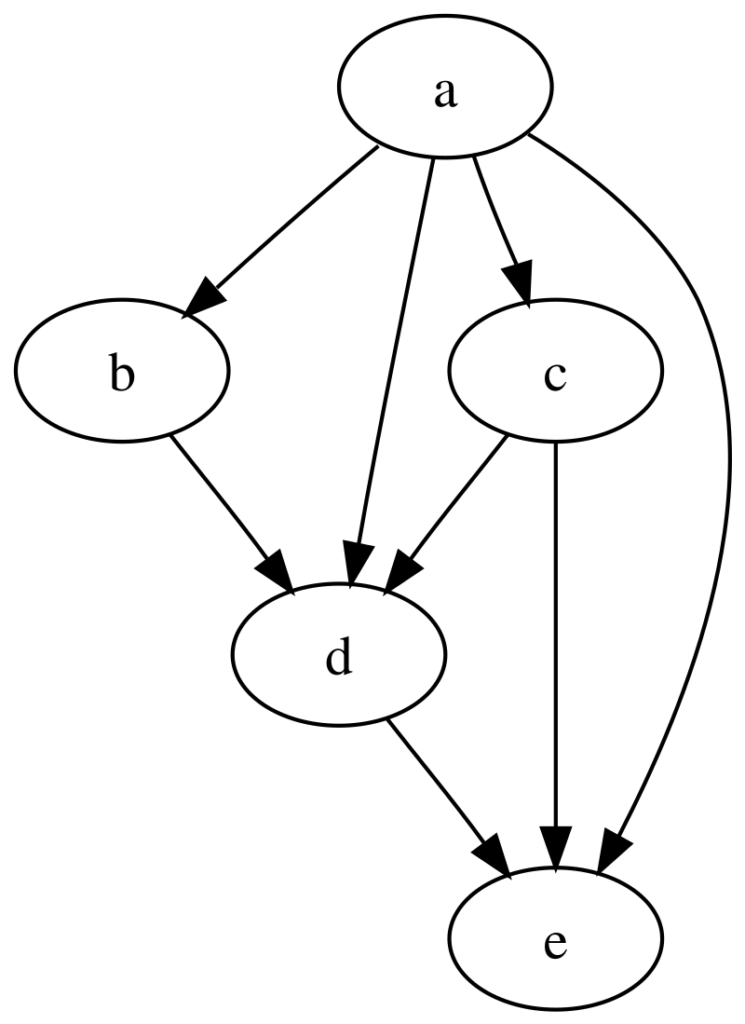
In other words, each edge has a dip and does not have cycles or in other words there is no path which goes back to the starting point. In relation with resources that deal with distributed ledger technologies, DAG takes the place for the main architecture of blockchain as a substitute.
Difference Between Blockchain and DAG
| Aspect | Blockchain | DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph) |
|---|---|---|
| Launch | Introduced in 2008 by Satoshi Nakamoto through the Bitcoin whitepaper. | Emerged in 2015, initially implemented by the NXT platform. |
| Structure | A sequence of blocks linked in a linear, unchangeable order. Each block must be verified and added one after another. | Uses nodes and edges to form a graph-like structure where each transaction links to several others. |
| Consensus Mechanism | Uses Proof of Work or other consensus models that rely on miners solving complex problems to verify transactions. | Transactions confirm previous ones, and users participate in validation, though they cannot confirm their own transactions. |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Can be expensive to use due to high transaction or gas fees, especially on popular networks like Ethereum. | Generally more cost-efficient, often with little to no transaction fees. |
| Transaction Speed | Slower due to block time, which is the delay between transaction creation and confirmation. | Much faster, as there’s no block time — transactions are confirmed continuously. |
| Transaction Validation | Miners or validators decide whether transactions are approved or rejected. | Transactions must confirm previous ones, creating a system where approval builds organically over time. |
| Popular Networks | Includes Bitcoin, Ethereum, and many enterprise-level private blockchains. | Used in platforms like IOTA (Tangle), NXT, and Byteball. |
| IoT Support | Not ideal for IoT applications due to slower speeds and higher fees. | Well-suited for IoT because it supports fast, low-cost transactions across many devices. |
| Microtransactions | Less efficient for small-value transactions due to high fees. | Designed to handle microtransactions effectively with minimal or no fees. |
| Large Payments | Reliable and secure for processing high-value transactions. | Less secure for large payments due to its semi-centralized nature. |
| P2P Energy Trading | Limited or no use in peer-to-peer energy trading systems. | Supports P2P energy exchanges, making it a preferred option for decentralized energy markets. |
Blockchain Features
Control is Decentralized: Blockchains operate using a peer-to-peer network instead of one associated with a central authority or server. Each participant has independent access and control.
Immutable: It is impossible to change or erase something once it is added to the blockchain. As a result, there is a reliable and unchangeable history of all data.
No Restrictions or Limitations: The ability for each network member to see every transaction builds trust and promotes openness.
High Level of Security: Data is protected with sophisticated encryption, guaranteeing all transactions are checked, and there is no possibility of alterations or fraud.
Allows Consensus Agreement: Verification of transactions is achieved by relying on agreement among participants in the network with the use of algorithms such as Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS).
Most Notable Areas of Blockchain Technology
Virtual Currencies: This is the most popular use of blockchain technology with Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies leading the way.
Logistics: Assists companies with tracking goods while also ensuring transparency for every step of the supply.
Self-Executing Contracts: Contracts guaranteed to execute when a set of predetermined rules is met, without needing a broker.
Healthcare Records: Ensures accessibility of medical data to relevant stakeholders while preserving confidentiality.
E-Voting: Supports the implementation of robust systems for voting security which increases confidence in elections.
Benefits of Blockchain
No Central Authority: With dispersed control, the likelihood of corruption or failure occurring at one point greatly diminishes.
Data Integrity: Trust is built in the accuracy of data because the information is reliable and permanently recorded without alterations.
Openness: Enhances responsibility within the system since each member in the network has access to the entire transaction record.
High Level Security: Security measures prevent unauthorized access, access by fraud, and protect data.
Improved Traceability: Tracking the history of an asset or transaction becomes straightforward which simplifies the auditing and verification process.
Challenges of Blockchain
Scalability Limits: Increased spending and decreased efficiency in transaction handling can result in difficulty managing a greater volume.
High Energy Use: Environmental and energy concerns can arise from certain mechanisms of building consensus like Proof of Work.
Technical Complexity: Understanding and implementing the technology may be more complex than most people prefer leading to slower adoption.
Regulatory Uncertainty: The absence of a single authority makes verifying compliance with laws and regulations particularly difficult.
Privacy Issues: Blockchain can disclose information in a transparent manner, but without the proper safeguards, it can reveal confidential data.
Here’s a uniquely paraphrased, copyright-free character of your paragraph relating to Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) features that is easy to read and comprehend.
Features of DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph)
Unidirectional Connections: In a DAG system, transactions are processed in a linear manner, which means each transaction “points” to other transactions in a certain predetermined direction.
No Repetition: In a DAG, every transaction points to the next one and there is no possibility of going back over already traversed paths. This increases efficiency since nothing goes around in circles.
Parallel Execution: Unlike blockchains, which must service transactions in a sequential fashion, DAG networks can execute multiple transactions simultaneously, resulting in superior speed and reliability.
No Miners Required: In most cases, with DAG-based platforms, users are allowed to validate transactions themselves which removes the necessity for miners, reducing energy consumption and hardware costs.
Improved Scalability: Since there are no blocks or chains used in a DAG, the structure and growth accommodates increasing data volumes and users without degrading performance.
Examples of DAG Applications
Cryptocurrencies: Through DAG technology, IOTA and Nano enable users to make rapid and cost-free everyday transactions.
The Internet of Things: Connected devices and sensors produce vast volumes of real-time data, which can easily be managed with a DAG structure.
Supply Chain Tracking: It assists in enabling corporations to keep track of inventory while in transit throughout the supply chain, increasing trust and visibility in the process.
Benefits of DAG Technology
Handles High Volumes: DAG networks are built to handle a large number of transactions simultaneously, which is ideal for speed and scale-dependent systems.
Fast Transaction Times: Confirmations occur much faster than in traditional blockchain systems, due to the absence of block waiting times.
Energy Efficient: Without miners, power-hungry processes are eliminated making the use of DAG platforms more environmentally friendly.
Low or No Fees: Due to the absence of mining and middlemen, users often pay little, to no transaction fees.
Adaptable Design: DAG networks are flexible and can easily withstand new requirements while supporting various forms of transactions.
Challenges of DAG
Technical Complexity: The structure of DAG can be more complex to set up and understand, potentially hindering mainstream adoption.
Security Risks: The newer approach of DAG lacks the tried and true security methods offered by older blockchain networks.
Limited Tools & Support: Users may discover a lack of developer tools and support communities still in the early growing DAG ecosystem.
Possible Bottlenecks: ‘Always on’ designs may aid in speed, but they do not prevent transaction processing delays from occurring during unexpected surges in activity.
Inconsistent Standards: Different DAG platforms have distinct circumscribed norms and rules, making interoperability assurance across networks a challenge.
Conclusion
Both Blockchain and DAG have made immense strides in technology for the safe and transparent handling of digital transactions, however they work in unique ways. DAG structures transactions like interconnected nodes which unlike Blockchain data that is organized into blocks, allows for faster, more scalable and cost-effective processing without the need for mining. The requirement of consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work (PoW) in Blockchain can potentially make things slower and more expensive.)
While well established in the security sector alongside cryptocurrency platforms such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, Blockchain lingers behind in speed paired with microtransactions and applications like the Internet of Things (IoT) and P2P energy trading which take substantial advantage of DAG.
In the end, it comes down to the specific use case to determine whether Blockchain or DAG is more suited. Immutability and high securoity? Blockchain is better. High efficiency paired with having to deal with low fees and exceptionally needing their automated systems? Then DAG will edge out on the competition.