I will discuss how to automate Bridging Aggregator Liquidity Management, and knowing how to automate cross-chain transactions and fund allocation will be necessary.
Eliminating manual processes and errors will allow real-time multi-chain liquidity management. Smart contracts and data feeds, which are widely available, can be utilized to manage rebalancing, ensuring seamless swaps with minimal risk and optimal capital utilization.
Understanding Bridging Aggregator Liquidity
Bridging aggregator liquidity refers to the pool of digital assets that bridging platforms pool to facilitate smooth cross-chain asset exchange. These aggregators link multiple blockchain networks, thus allowing users to exchange different tokens without the need for a liquidity source.

Efficient liquidity guarantees that swaps are executed promptly, with insignificant slippage and the best possible pricing, while also decreasing the likelihood of transaction failures. Manually controlling this sort of liquidity is challenging due to the dynamic nature of token supply, transaction volumes, and cross-chain fees.
Projects and traders who grasp the inner workings of bridging aggregator liquidity are able to make better decisions about the allocation of capital, trading efficiency, and ease of access across chains.
How to Automate Bridging Aggregator Liquidity Management

Example: Automating Liquidity for a Cross-Chain Aggregator
Step 1: Assess Liquidity Needs
- Look through transaction history and volume to understand how each blockchain was used over time.
- Determine which token pairs require liquidity fills the most to minimize slippage.
Step 2: Choose an Automation Tool
- Select a bridging aggregator tool that offers an automatic function, such as Orbiter Finance or deBridge, or utilizes automated custom smart contracts.
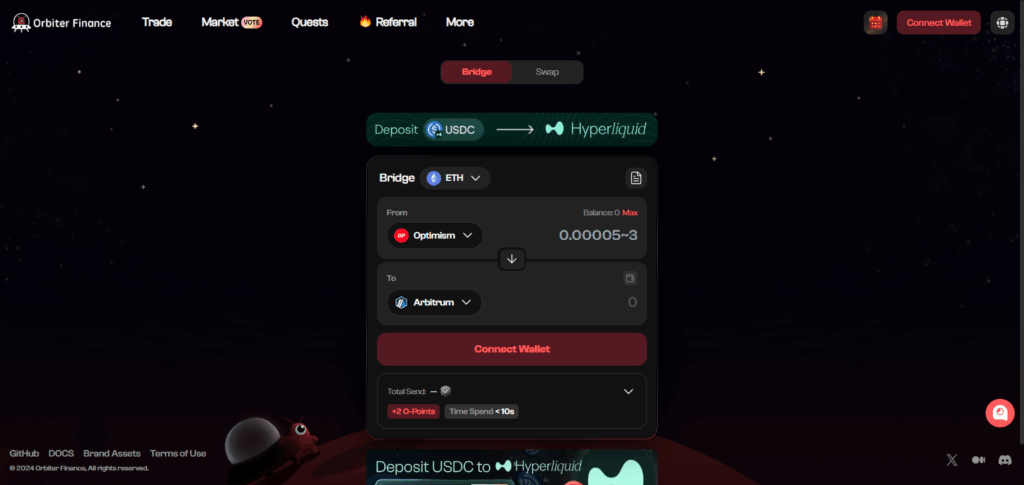
- Ensure the tool can track multiple chains simultaneously.
Step 3: Integrate Real-Time Data Feeds
- Set up APIs that track token index prices, liquidity pools, and transaction volumes.
- Make sure the data updates in real time so that funds can be allocated correctly and so that assets are not wasted.
Step 4: Set Rules for Fund Allocation
- Set min and max thresholds for liquidity overall and for each token pair.
- Set up automatic rules to balance funds between blockchains when it is necessary.
- Set slippage control rules to minimize exposure in high volatility conditions.
Step 5: Deploy Smart Contracts
- Distributing funds, automatic balancing, and swaps through smart contracts need to be in the contracts.
- Ensure that the smart contracts include security provisions to prevent unauthorized access.
Step 6: Monitor & Optimize
- Look through the information displayed on the screens and upper management sections.
- Adjust the rules on demand and trading fees, and then monitor the trading volume to determine what works best.
- Set notifications for low liquidity or other unusual activities.
Step 7: Ongoing User Testing
- Occasionally, use the automation tools to run test swaps and verify their functionality.
- Continue to adjust the limits and rebalancing tactics as long as they remain functional.
Key Components of an Automated Liquidity System
Here’s a systematic approach on constructing an automated liquidity system for bridging aggregators as listed below.
Liquidator Tech – Automatically manages the collection of funds as well as the swaps and rebalancing of the funds.
Centralized and Decentralized liquidity pools – Available for use within a specific or within a borderless environment.
Data Feeds – Converts pools of cross-chain assets into real-time reports.
Demand and Supply – Triggers the automatic movement of liquidity for specific chains or token pairs.
Drop Calculation Devices – encloses slippage and transfer loss.
Live Tracking Windows – Pinpoints areas of inactivity.
Benefits of Automating Liquidity Management
Below are the benefits liquidity management automates get access to.
Increased Efficiency – Faster processing speeds with no human interaction involved.
Reduced Human Error – Transaction balancing errors that often happen with little tracking or supervision get resolved.
Optimized Capital Utilization – More resources get allocated towards productive tasks with less funds being dormant.
Real-time Monitoring – The account’s liquidity, stocks of available tokens, and active markets get updated live.
Dynamic Adjustments – Shifting on to other chains and adapting to other volatility and demand shifts is instant.
Lower Operational Costs – Avoid tasks that need constant human interaction and duplicates.
Enhanced Risk Management – Set thresh holds, slippage alerts, and loss control markers for better loss prevention.
Risk & considerations
Smart Contract Vulnerabilities
Losing money on breaches or mishaps on automation contracts can happen easily and quickly.
Cross-Chain Risks
In case of any chain liquidity discord, the other chains could be impacted.
Slippage and Price Volatility
Losing money when the worth fluctuates. Online purchases can be abused if not monitored.
Over Reliance on Automation
Relying too heavily on automatic systems can overlook the possibility of mistakes or unusual movements.
Liquidity Imbalance
Improper slippage thresholds can lead to shortages on chains and pairs of tokens on certain chains.
Network Fees and Gas Costs
Statement, Withdrawal, and Payment Fees can result in substantial financial penalties.
Monitoring and Alerts
Watching the frequent automated attacks and kept footsteps not continuously monitored.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Ignoring Cross-Chain Fees — Gas prices affecting profitability depends on ignored fees.
Over-Allocating to One Pool — Single chain or token pair liquidity concentration is more risky.
Neglecting Monitoring — Complete automation as an only monitoring strategy is problematic.
Poorly Defined Rules — Thresholds set incorrectly for rebalancing or slippage lead to huge losses.
Skipping Security Audits — Smart contracts still untested lead to fund hacks more often.
Infrequent Updates — Stagnating on unchanging strategies drop the strategy efficiency considerably.
Overcomplicating Automation — Excessive layers generate more mistakes and confusion.
Future of Automated Liquidity Management
In the field of bridging aggregators, the automated management of liquidity undoubtedly holds the promise of more major developments, owing to innovations in AI, machine learning, and cross-chain interoperability.
AI-driven systems will facilitate predictive liquidity allocation, reallocating funds in real time to reduce market-swing slippage, boost demand, and achieve optimal efficiency. Advanced protocols will enable less-risky and more time-efficient cross-chain blockchain operations.
Further, deflationary DeFi systems will likely to deploy automation systems with sophisticated analytics as well as improved risk mitigation strategies. Over time, greater accessibility automation will evolve to make liquidity management even faster, easier, and highly dependable to traders of all sizes.
Pros & Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Increased Efficiency – Automates fund allocation and cross-chain swaps, saving time. | Smart Contract Risks – Vulnerabilities or bugs can lead to fund loss. |
| Reduced Human Error – Minimizes mistakes in rebalancing and liquidity tracking. | Over-Reliance on Automation – May overlook unusual market conditions or anomalies. |
| Optimized Capital Utilization – Ensures liquidity is allocated where it’s needed most. | Network Fees & Gas Costs – Frequent automated transactions can be costly. |
| Real-Time Monitoring – Tracks liquidity, token availability, and market changes instantly. | Complex Setup – Initial integration and configuration can be technical and time-consuming. |
| Dynamic Adjustments – Adapts to market volatility and changing demand automatically. | Cross-Chain Risks – Failures or delays on one chain can affect overall liquidity. |
| Enhanced Risk Management – Implements slippage limits, thresholds, and alerts to prevent losses. | Requires Ongoing Monitoring – Automation still needs supervision to detect anomalies. |
Conclusion
In summation, the automation of bridging aggregator liquidity management is necessary for optimizing cross-chain transactions, minimizing risk exposure, and increasing the efficacy of operations.
The use of smart contracts along with predictive analytics, real-time data feeds, and automated rebalancing functionality makes it possible for projects to distribute liquidity efficiently across multiple chains while minimizing slippage and transaction failures.
Loss prevention and system reliability through constant monitoring and calculated risk management is necessary. When considering the evolution of the DeFi space, it is clear that automated liquidity management solutions save time and costs, which reduces the effort and risk associated with cross-chain trades.
FAQ
Why should liquidity management be automated?
Automation improves efficiency, reduces human error, optimizes fund allocation, and ensures real-time adjustments across multiple chains.
Which tools can help automate liquidity management?
Smart contracts, bridging aggregators like Orbiter Finance or deBridge, cross-chain APIs, and analytics dashboards are commonly used.
What risks should I consider?
Smart contract vulnerabilities, slippage during volatility, cross-chain delays, and network fees are key risks to monitor.