In this article, I will address the question Are bridging tokens safe? With the increase in cross-chain activities, token bridges have become critical for transferring assets from one blockchain to another.
Security breaches alongside other emerging concerns have made users, and for good reason, skeptical. We will examine the functions of bridges, their inherent risks, and the optimal strategies for safeguarding your assets while bridging.
What Are Token Bridges?
Bridges that interact with blockchain tokens function as both platforms and protocols for alphanumeric tokens transfer between different blockchains.
They inter operate with each other. Token bridges work by locking tokens on one blockchain and issuing equivalent tokens on another. In this way, users can transfer assets like cryptocurrency from one blockchain to another without a centralized exchanging firm.
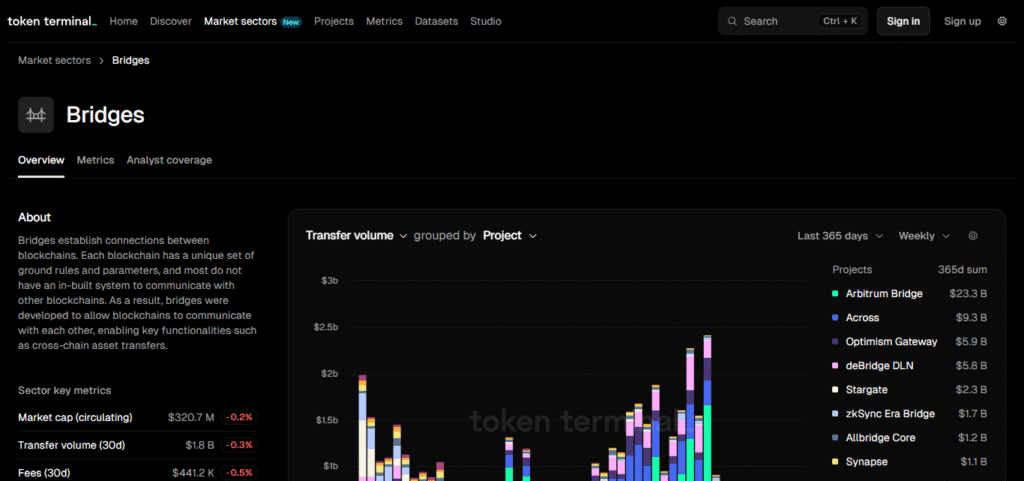
Bridges play an important role in connecting diverse networks i.e. enhancing the scalability and flexibility of blockchain ecosystems such as Ethereum enhancing flexibility to Binance Smart Chain. Different ecosystems are each served by a different bridges such as Wormhole, Polygon Bridge and Avalanche Bridge.
How Token Bridges Work
Locking Tokens
- Each user starts the process of transacting from one blockchain to another using the bridge platform.
- The tokens on Blockchain A are locked in an escrow account or a smart contract. This means that the tokens are not accessible for withdrawing or transactions on Blockchain A during the transfer.
Wrapped Tokens
- The bridge then proceeds to issue equivalent tokens on Blockchain B. The term “wrapped tokens” or “synthetic tokens” is used to refer to these new coins.
- These wrapped tokens “originate” from the tokens which have been locked and hence they are bound to their value.
Transfer and Confirmation:
- The bridge also takes care that the number of wrapped tokens generated on Blockchain B is equal to the number of locked tokens on Blockchain A.
- After confirming this, users can make transactions with the new tokens they have on Blockchain B.
Unlocking Tokens (Optional)
- The process of users moving tokens back to Blockchain A is almost the same. Wrapped tokens are burned on Blockchain B, after which the original tokens are unlocked and sent back.
Is Bridging Tokens Safe
Bridging tokens have their own risks even when they can be deemed as safe. In 2025, several bridges will improve their security through better smart contract design, decentralization, and auditing. However, poorly monitored bridges and centralized ones still contain gaps.
The hacks from the past remind us that a certain level of trust needs to be placed on some platforms which have clear processes. For user safety, confirming official URLs, sending limited initial transfer amounts, and utilizing hardware wallets are all crucial steps.

No method is devoid of risk, but following gold standard procedures along with choosing the right reputable bridges lessens the risk of loss greatly. All in all, bridging is considerably safer now than it used to be, but still requires responsibility.
How Safe Are Token Bridges in 2025?
The safety of token bridges has improved between 2025 and my previous inputs due to advancements in smart contract security, decentralized validation, and increased auditing in technology security.
Numerous top bridges now utilize diversifying security like decentralized oracles, multi-signature systems, and real-time suspicious activity monitoring systems that detect and respond to threats. Still, risks are not completely gone.
Bridges that remain centralized continue to have single points of failure, while exploitable weaknesses in smart contracts can be configered. Asset bridges, which are newer, have better modern technology but users still need to be careful, using reliable platforms and adhering to security best practices.
Best Practices for Safely Bridging Tokens

Use Trusted Bridges: Always go for reputable bridges with high popularity in the community and positive history of use (e.g., LayerZero, Wormhole, Polygon Bridge).
Double-Check URLs and Contracts: Ensure you are using the official website of the bridge. Use verified aggregator platforms or DeFiLlama which can be trusted to have accurate contract addresses.
Check for Audits and Transparency: Use only those bridges which make known the audit details of their bridges and publish them through independent security testing firms.
Start with Small Transfers: Before sending large numbers, ensure the system works by conducting tests with small amounts.
Put Safety First when it Comes to Wallets: Do not disclose your private keys or seed phrases and opt for hardware wallets which provide extra safety.
Keep and Eye on Gas Fees along with the State of the Network: Risk of delays as well as unsuccessful transactions may arise when the bridge is used during periods of suspicious activity across the network.
Stay Abreast: Make it a habit to follow related social media handles as well as news to help remain updated on information regarding exploits, updates, or system downtime.
Pros And Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Enables cross-chain interoperability | Vulnerable to smart contract bugs or exploits |
| Avoids relying solely on centralized exchanges | Some bridges are centralized (single point of failure) |
| Faster and often cheaper than CEX transfers | Past bridge hacks have resulted in major losses |
| Growing ecosystem and improved tech in 2025 | Risk of using fake or scam bridge websites |
| Many bridges are now audited and transparent | Transactions can fail or get delayed under congestion |
Conclusion
In conclusion, bridging tokens has become safer than ever in 2025, yet it still carries dangers, such as hacks and smart contract weaknesses. Users can reduce threats by using reputable bridges, checking links, and adhering to industry standards.
Although not devoid of risks, cautious bridging within today’s dynamic crypto environment is safe for most users looking for cross-chain interoperability.










